Stay updated on the latest trends and innovations in modern construction, building methods, and advanced technologies transforming the industry today and beyond.
For companies, inventory management has always been a major difficulty, but recent technological developments have created new opportunities. One revolutionary tool that lets businesses monitor and control their inventory without physical location ties is remote inventory management. Real-time data availability, cost-effectiveness, and improved asset control are just a few of the clear benefits this change from conventional approaches presents. The main advantages of using remote inventory management will be discussed in this post, together with the tools enabling it and the trends reshaping inventory management for the future.
What is Remote Inventory Management? An Overview
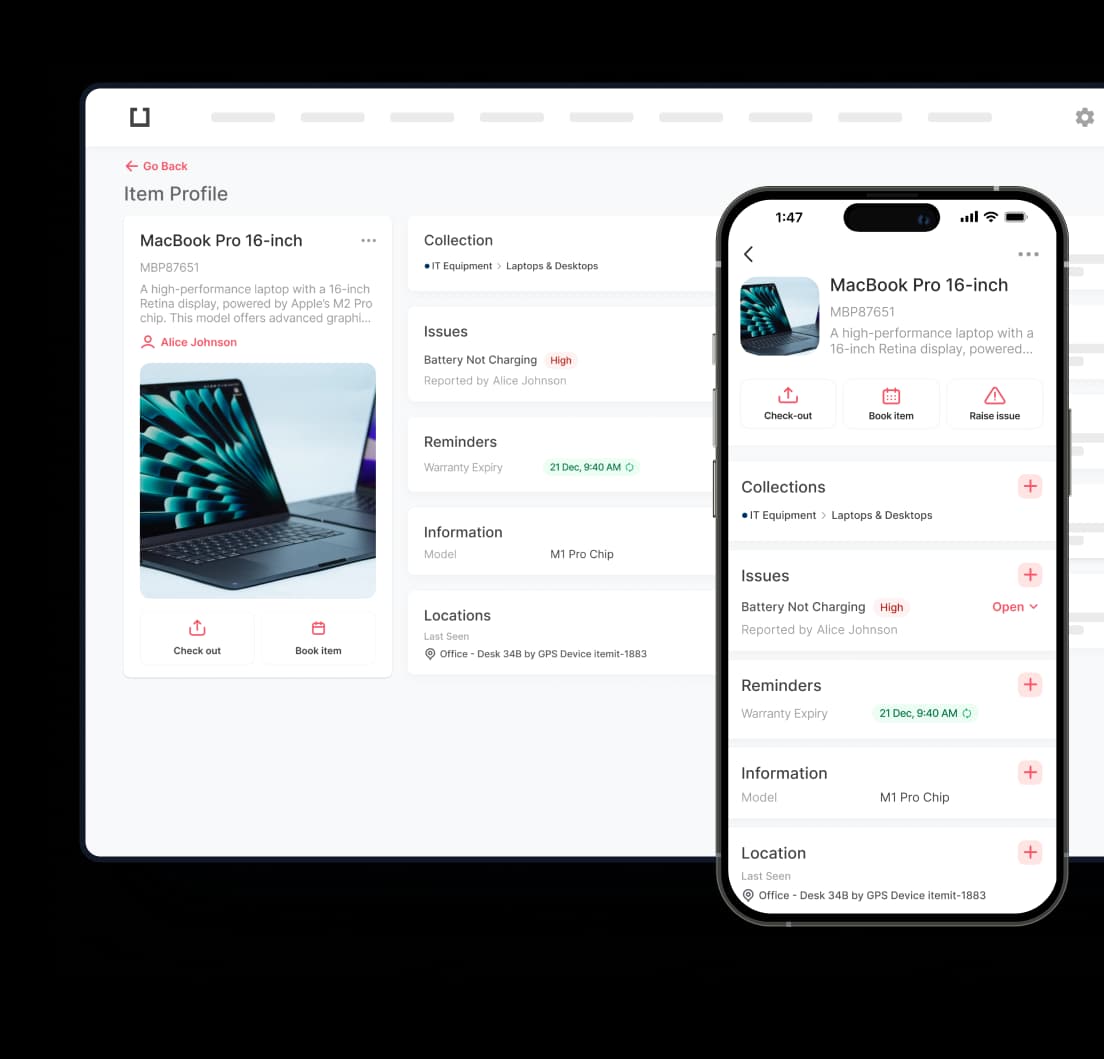
Thanks to cloud-based technology, IoT devices, and mobile apps, remote inventory management – a modern solution that lets companies monitor and control their inventory from anywhere – is possible. Without physically being in the warehouse or storage facility, this method allows businesses to manage remote equipment in real-time, therefore providing fast access to inventory data, updates, and insights. From conventional approaches, where inventory control was generally manual, labour-intensive, and limited to on-site operations, this system marks a major departure.
Tasks like stock counts, order tracking, and inventory changes in conventional inventory management call for direct human engagement, usually resulting in mistakes and inefficiency. Conversely, remote asset management uses technology to automate these chores, therefore providing companies with real-time data access, greater accuracy, and easy management of remote assets. Remote inventory management is a more dependable and effective solution for contemporary companies since this difference in approach not only lowers the effort but also improves decision-making capacity.
Main Benefits of Remote Inventory System Use
Using a remote inventory system has many advantages that will help companies control their inventory greatly. Real-time tracking is among the most apparent benefits. Businesses can track their inventory levels as changes occur by means of a remote inventory tool, therefore offering instantaneous updates on product availability, movement, and position. Maintaining ideal inventory levels, preventing stockouts, and guaranteeing that items are accessible as needed all depend on this ability. By use of precise and timely data, real-time tracking also enhances decision-making by enabling companies to react swiftly to operational needs and market demand.
Receiving remote inventory updates also has other major advantages – for example, passive cost savings. High operating costs, including human resources, transportation, and storage charges, abound in traditional inventory control. Using a remote inventory system helps companies simplify these procedures, therefore lowering the need for manual data entry and physical inventory audits. This reduces labour costs as well as the possibility of mistakes that can cause expensive disparities and inefficiencies. Furthermore, lowering the demand for massive, centralised warehouses and, hence, lowering storage costs means the ability to control goods remotely.
Using a remote inventory system also greatly increases productivity. This depends heavily on automation since the system itself can now manage numerous chores that once required human input. Reorder points, for instance, can be dynamically changed depending on real-time inventory levels, guaranteeing that stock is replaced without overordering. Using a remote inventory solution helps one conduct inventory audits more swiftly and precisely, extending efficiency even in these audits. The outcome is a more simplified inventory control system that increases general output while saving time and money.
Moreover, remote inventory control lets one be more flexible and scaled. The demands of inventory control change with a company's size. Without a full revamp of current procedures, a remote system can rapidly adjust to these changes, allowing new sites, products, and supply chain complexity. This scalability guarantees that as the company grows, the system will stay efficient and effective, so it is a wise long-term investment.
All things considered, implementing a remote inventory system has significant benefits. It provides scalability, cost cuts, real-time tracking, and more efficiency. These advantages make remote inventory control a necessary tool for companies trying to be competitive in today's fast-paced market and maximise their operations.
Understanding Remote Inventory Monitoring and How It Works
Using cutting-edge technologies and methods, remote inventory monitoring – that is, Monitoring inventory levels, movements, and conditions from a distance – allows companies to control inventory remotely. This method guarantees current stock information without requiring their physical presence at the inventory location. Remote inventory monitoring is essentially meant to improve asset visibility and management, therefore lowering the risk of mistakes, loss, and inefficiencies.
How Does Remote Inventory Monitoring Work?

Remote asset monitoring makes use of a mix of tools and technology cooperating to offer real-time data and insights. The salient features are broken out here:
-
- IoT (Internet of Things) Devices: Common applications for sensors and RFID tags in asset remote monitoring are tracking inventory item location, condition, and status. These devices forward data to a centralised system, enabling managers to track supplies from a distance.
- Cloud-Based Platforms: Usually, IoT device data is kept and handled on the cloud. This helps companies access inventory data anywhere, at any moment. Additionally, cloud systems provide scalability—that is, growth within your company.
- Mobile Applications: Mobile apps help inventory controllers view real-time data on their tablets or cell phones. Often including dashboards, reporting tools, and alarms, these apps help make remote inventory management easier.
- Barcode and RFID Scanners: Barcode and RFID scanners are crucial for tracking unique objects inside inventory. Scanning barcodes or RFID tags allow companies to rapidly change their inventory records, guaranteeing accurate and current data everywhere.
- AI and Machine Learning: Advanced systems might use artificial intelligence and machine learning algorithms to examine inventory data, project trends, and autonomously control inventory levels. AI can, for example, recommend reordering points and help detect trends in stock movements, thereby guaranteeing effective maintenance of inventory levels.
Examples of Remote Inventory Monitoring in Action
- Retail: To monitor stock levels at all of its sites, a retail chain employs a cloud-based inventory management system. When stock levels drop below a designated level, the system notifies the central warehouse and initiates automated replenishment.
- Manufacturing: IoT sensors let a manufacturing organisation monitor raw material conditions in several warehouses. Tracking temperature and humidity, the sensors send alarms when conditions stray from the specified ranges, preventing rotting and guaranteeing quality.
- Healthcare: Critical medical supplies and equipment are tracked in a hospital using RFID technology. Remote asset monitoring helps the hospital guarantee that necessary supplies are always available when needed, lowering downtime and enhancing patient treatment.
Remote inventory monitoring is a great solution that lets companies use IoT devices, cloud platforms, mobile apps, and sophisticated analytics to control inventory from anywhere. These technologies help businesses improve inventory control, visibility, and efficiency in their systems of operations.
Remote IT Asset Management and Its Role in Remote Inventory Management

Remote IT asset management is the practice of employing remote IT asset management software from a centralised location to monitor, track, and control IT assets, including PCs, servers, software licenses, and network devices. This method is absolutely essential for remote inventory control for companies with distant work environments. Remote IT assets are housed in employees' homes, branch offices, and data centres, among other sites.
Remote IT asset management guarantees that independent of their physical location, all IT resources are accounted for, maintained, and optimised, therefore supporting remote inventory management. From acquisition to deployment, maintenance, and ultimate disposal, this entails following the life of every asset. This helps companies to keep a clear awareness of their IT inventory, lower their asset loss or theft risk, and guarantee adherence to software licensing and security policies.
Why Remote IT Asset Management Is Essential in Systems of Distributed Work
Managing IT assets remotely has become more critical in the increasingly remote and hybrid work settings of today. This explains:
- Visibility and Control: Remote IT inventory management software offers real-time insights into where each asset is situated, who is using it, and its present state. Therefore, it helps to maintain visibility over IT assets even while staff members work from different sites without a centralised system. This degree of visibility depends on making educated judgements on asset allocation, maintenance, and improvements.
- Compliance with Security: Maintaining security and compliance depends primarily on remote management of IT resources. Remote IT inventory management tools help companies track software upgrades, enforce security policies, and guarantee that every gadget conforms to corporate standards. Protecting sensitive data and making sure all IT tools follow legal criteria depend notably on this.
- Cost Efficiency: Effective remote management of IT assets helps companies maximise their use, cut needless waste on duplicate or underused assets, and extend the lifetime of their equipment. In addition to saving expenses, this guarantees effective resource use, therefore supporting general operating efficiency.
Support and Maintenance: It might prove difficult to provide timely support and maintenance for IT assets in a remote work environment. Without physical access to the equipment, remote IT asset monitoring systems let IT staff diagnose and fix problems, apply software upgrades, and perform routine maintenance chores remotely. This ability reduces downtime and maintains staff productivity, regardless of location.
Trends Shaping the Future of Remote Inventory Systems

Several important themes will help to define the direction of remote inventory management, including remote IT asset monitoring:
- AI and Machine Learning Integration: Remote IT asset management software's predicted increasing usage of artificial intelligence and machine learning will help to enable predictive maintenance, automated asset tracking, and more intelligent resource allocation. These technologies enable companies to maximise asset use depending on real-time data and predict problems before they develop.
- Increased Focus on Cybersecurity: Cybersecurity will always be a top concern, even as remote work becomes increasingly common. Future remote inventory systems will probably include stronger security elements to guard IT assets from cyberattacks, such as automated compliance checks, real-time threat detection, and improved encryption techniques.
- Expansion of IoT Devices: Remote inventory management will continue to evolve, driven by the explosion of IoT devices. Together with sophisticated analytics, these tools will offer even more detailed insights into asset conditions and consumption patterns, helping companies control their inventory more precisely and accurately.
- Cloud-Based Solutions: The trend towards remote asset management software for IT housed in clouds should quicken. Cloud platforms will enable simpler connections with other company systems, hence enhancing general operational effectiveness. They will give companies easily available, scalable, flexible solutions that fit their particular requirements.
In essence, managing inventory remotely depends on remote IT asset management, especially in today's distributed work environments. Businesses can guarantee that their IT assets are safe, compliant, and performance-oriented by using remote technology asset control software and keeping ahead of developing trends, therefore supporting more general objectives of operational efficiency and cost-effectiveness.


Modern Methods of Building Construction. Trends and Innovations to Watch

How to Create an Effective Construction Management Plan for Your Project
Create an effective construction management plan that improves safety, minimises delays and keeps your project organised and on track from planning to completion.

A Complete Guide to Construction Cost Management and Planning
Effective construction cost management and planning improve profitability, enhance financial stability, and strengthen resource allocation across every project.