Your IT assets are crucial in keeping your business running, now more than ever.
Firstly, we need to find out what an IT asset is so we can manage and register them properly.
IT assets are fundamental elements of the modern business landscape, including everything from hardware to intellectual rights and data. These resources form the basis for operational efficiency, strategic growth and innovative development of organisations. Good IT asset management is a powerful tool for cost optimisation and an important strategic advantage in the dynamic, changing technological world.
What Are the Different Types of IT Assets?
IT assets include physical components (hardware and servers), software, intellectual property, licenses and data. Core resources:
- Physical IT assets - computer equipment, servers, network devices and other technological components. Provide physical infrastructure for data storage and processing.
- Software IT assets - different types of software, from operating systems to specialised applications. Serve to perform specific tasks and functions within the organisation.
- Intellectual IT assets - patents, trademarks, copyrights and other forms of intellectual property related to technologies.
- Data stored and processed in the organisation is also a valuable IT asset. This includes customer base, financial information, research, and more.
What is IT Asset Management?
IT asset management (often referred to as ITAM) is the process of registering, deploying, maintaining, modernising, and finally disposing of an organisation's assets. Simply put, this process verifies that an organisation's values (both tangible and intangible) are tracked and actually used.
Looking closer at an IT asset, what do we have? In general, such a resource may be equipment, software, or information of value to the organisation. For example, in the Atlassian IT department, one of the most valuable assets is the computers and software licenses that allow us to build, sell, and maintain our own software and the servers on which it is hosted.
IT assets have a finite period of use. To get the most benefit from them, you need to actively manage their life cycle. Each organisation can define its own phases of this life cycle. These typically include planning, procurement, deployment, maintenance, and decommissioning. In IT resource management, it is important to apply this process at all stages of the life cycle to determine the total cost of ownership and optimise resources.
In the past, IT departments could manage resources in their own systems. Now, the management of the organisation's resources goes far beyond equipment with official certification marks. The subscription-based software and the desire of employees to configure work tools through application stores pose new challenges for resource management. Teams are now working in a way that IT employees have to be flexible and adapt the resource management process to achieve maximum company efficiency.
Employees of various profiles are eager to work with the tools that are most suitable for solving current problems. Resource management is an even more important component of the organisation’s overall strategy to reduce risks and costs. With a single reliable source of information, the process of resource management is indispensable for optimising the budget, supporting life cycle management and making decisions that affect the organisation as a whole.
What is an IT Asset Register?
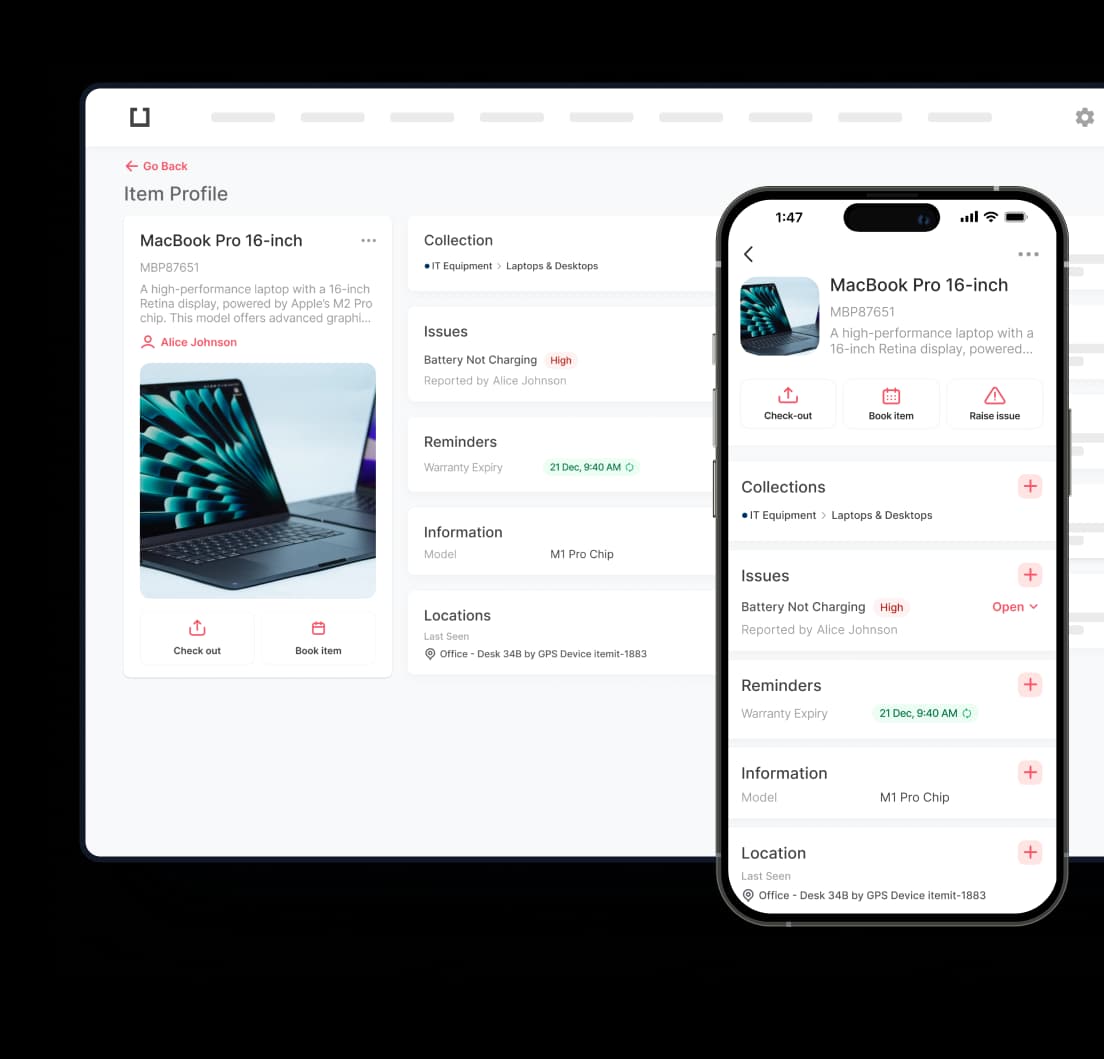
IT asset register meaning is not quite difficult to comprehend. An IT asset register definition states that it is a tool where you log and monitor your IT hardware, PCs and equipment. An IT asset register not only allows you to track your assets in real-time, but also allows you to run custom reports on what hardware the business has and who has it.
With an IT asset register, you’ll also be able to view, edit, and share any information related to each asset. Permissions are customisable, so any sensitive information can remain hidden. This can include any financial information, user manuals, warranty dates, which assets are booked out, and any other information you require.
Why Should You Track Your IT Assets?
In the high-speed digital environment of today, companies of all dimensions rely on a wide variety of IT assets, from hardware like servers, laptops, and mobile devices to software applications and cloud services. Managing them effectively is essential for ensuring smooth and uninterrupted operations, thus minimising the chances of downtime and optimising resource use. This is where an IT asset register comes into play.
An IT asset register is, therefore, a very important tool for an organisation in the systematic tracking and management of IT assets. In the absence of such a register, organisations across the business spectrum tend to face a number of issues, including but not limited to improper allocation of resources, unexpected expenses, and compliance risks. It helps in reducing these problems by providing a single centralised record of all IT assets across the enterprise that is accurate and current.
IT asset registers allow a business to identify the installations, locations, and uses of the assets and whether they can be replaced or upgraded. This will help them in effective budgeting and procurement planning. IT resources identified in this way could be aligned with organisational goals. Additionally, the IT asset register becomes very critical in terms of compliance with industry regulations and standards, as proof of compliance with respect to data security and software licensing requirements can be provided through its use.
IT asset registers are basically required because of the increasing complexity entailed in managing IT resources amidst dynamically changing technology. This forms the foundation for developing a strong strategy for IT asset management, which is sure to yield efficiency, save costs, and promote good decision-making.
What Should Be Included in Your Asset Register?
The IT asset register is not just a list or an inventory of devices; rather, it is a detailed record of every asset. Elements that should be included in an IT asset inventory make the register functional, informative, and valuable for any decision-making. The outline below shows the critical components that comprise an effective IT asset register:
You’ll also be able to tag your computers and devices with QR code asset tags. This allows for instant identification of each piece of equipment so you can quickly see who an asset belongs to and where it’s supposed to be. Every time a QR is scanned, the asset’s location is updated.
2. Description of the Assets
It provides detailed descriptions attached to each IT asset, which include the type, such as laptop, server, or software, manufacturer, model, and specification, among others. On software assets, it may further include version number, type of license, number of users, or seats.
This component maintains all the financial information related to the asset, like the date purchased, cost, supplier, and warranty. Purchase detail tracking is critical to planning and budgeting and enables financial reporting related to the replacement or upgrading of an asset.
Knowing where each asset is located is an important part of managing physical assets. The register should record the physical location of the asset, such as the office, department, or even room and desk. In the case of mobile assets, like laptops and tablets, tracking the user or department to which the item is assigned may be of equal importance.
Asset tracking made easy.
When you’re onboarding staff, IT asset management software lets you track IT hardware that is given to every colleague. You then have a permanent and accurate record of where your equipment is, who has it and even where it is.
6. Create a Fixed Asset Register
Once you have an IT asset register for your business, you can incorporate this into your fixed asset register. This confirms you know how much your IT hardware and computers are worth and guarantees all equipment is correctly accounted for.
7. Lifecycle and Depreciation
Every IT asset has a life cycle, from acquisition to retirement. The register should monitor the different life-cycle stages of the assets, including deployment, status, upgrades, and eventual decommissioning or disposal. Moreover, it should also capture depreciation information, which will be helpful in managing financial reporting and replacement planning.
Managing IT inventory helps to ensure your company is GDPR compliant. This includes knowing which IT assets everyone is using and what personal data is collected, stored or processed on each device. This is to ensure that only those members of staff who are authorised to access such data have the ability to do so. An IT asset register can help you keep on top of this quickly and easily.
9. Security and Access Controls
The record should also include details regarding the security measures and access controls over each asset. This would contain details of encryption, details regarding several user access levels, and security incidents related to the assets. Proper documentation of security controls helps safeguard sensitive data and ensures conformance to the best practice of regulatory compliance.
10. Audit and Reporting Features
An IT asset register needs to have features for auditing and report generation. Regular audits assist in verifying the register's accuracy and allow for the detection of discrepancies; reporting features enable managers to generate insights related to asset use, depreciation, maintenance, and others, all for informed decision-making.
The elements combine to give an overview view of an organisation's IT assets. The detail and accuracy of record-keeping in an IT asset register guarantee enhanced asset management processes and improved operational efficiencies, which in turn allow for better strategic decisions.
How Do You Create an IT Asset Register?
Implementation of the IT asset register is something of a strategic nature, and it requires detailed planning, effective collaboration, and proper apparatuses for its implementation. Only then can an organisation efficiently and effectively manage its IT assets. In that way, it will be able to track, manage, and optimise its IT assets so as to drive efficiency and cost reductions. The following is a step-by-step guide on how to implement an IT asset register:
1. Description of objectives and scope
But before implementing it, one needs to specify the objectives for which an IT asset register is kept. Decide what you want: improved asset tracking, better compliance, or enhanced budget management. Also, define the scope of the register: Will this include only hardware, or are you going to track software, licenses, and cloud services?
2. Build a Cross-Functional Team
An IT asset register requires input from the IT, finance, procurement, and legal departments. To ensure all facets of asset management are covered, organise a cross-functional team of representatives from each of the above-mentioned areas. This team will guide the implementation process and make key decisions.
3. Choosing the Right Tool
The right tool or software for creating and maintaining the IT asset register is paramount. Seek one that is user-friendly, flexible, and has an affiliation capacity with existing systems. In choosing a tool for this, look for features such as automated tracking, real-time updating, reporting, and compliance management.
4. Inventory Your Existing IT Assets
This shall be followed by a comprehensive inventory of all the existing IT assets. In other words, each piece of hardware, software, and service in use needs to be discovered and documented. This inventory process should record all the requisite information: asset identification, descriptions, locations, and user assignments.
5. Asset Identification and Tagging
Once the inventory is complete, establish a system for asset identification and tagging. Tag each item with a unique identifier, whether this is an asset ID, barcode, or QR code. This will make it easier to keep track of the assets within the register and enable one to locate and reference them instantly.
6. Populate the Asset Register
Now, using the inventory data and identification system, you can start populating the IT asset register. At this stage, all collected data should be entered into the selected tool, ensuring each constituent component is captured, such as asset descriptions, purchase information, and lifecycle details. Check for completeness and accuracy to avoid discrepancies later on.
7. Define Processes and Responsibilities
Define transparent processes and delegate tasks to responsible parties to ensure that an IT asset register runs smoothly and sustainably. Clearly spell out who updates the register, carries out regular audits, manages maintenance schedules, and ensures compliance. Such workflows and protocols must be set up to sustain the register's integrity and accuracy over time.
Properly train all those involved in managing and using the IT asset register. This includes how to operate the chosen tool, adding information to an asset register, and creating reports. This is a continuous process; refreshing and updating must take place from time to time when new features or processes are introduced.
9. Conduct Regular Audits
Run audits regularly to maintain the accuracy and currency of your IT asset register. Schedule periodic audits of the assets listed in the register with actual physical assets that are in use. Auditing will reveal inconsistencies - either an asset not found or incorrect data - that can be rectified immediately.
Once the IT asset register is up and running, its effectiveness must be continuously monitored for opportunities to optimise. Look within the register for trends, resource allocation, and future needs. Check the performance of the register against the laid-down objectives from time to time and adjust it accordingly.
11. Ensure Ongoing Compliance
Compliance issues are particular to matters of licenses on software and data security. Leverage IT asset register to track licensing, renewal dates, and security. Implement processes and procedures that enable the organisation to follow the regulations of both industries it serves, avoiding fines or other potential legal concerns.
Best Practices for Managing an IT Asset Register
Proper management of an IT asset register is important in ensuring the efficient use and security of your organisational IT resources in your business. Listed below are best practices to be followed while maintaining an IT asset register towards its accuracy and completeness:
1. Accuracy and Completeness
This is one of the most important things relating to any management of the IT asset register: making sure that all information in it is complete and accurate. Keep updating the register from time to time when there are changes in the status of the assets, like new acquisitions, disposals, or transfers. Ensure that all the assets are recorded, detailing a given asset with its current location, user, or condition.
2. Automate Where Possible
This is where automation can make a real difference in reducing the effort associated with managing an IT asset register. Useful automated tools can track and update information on assets, especially dynamic ones like software licenses and cloud services. Automation reduces manual error and allows for real-time updates that free up resources for more critical endeavours.
Run regular audits against your IT asset register to check for its accuracy. Audits must count the physical assets or the software in use against records in the register, checking for any differences. Such regular audits will help in keeping the integrity of the register and also appear to unravel a variety of issues, including the loss of assets or fitting of unauthorised software.
4. Robust Security Measures
Since this IT asset register might hold sensitive data or critical infrastructure, security is paramount. Design appropriate access controls to ensure that only authorised personnel have the ability to edit or even view an asset register. Of course, the register should be encrypted and have regular backup processes in case of data loss or breaches.
5. Standardise Data Entry and Classification
Standardising data entry and classification in the IT asset register will avoid confusion and ensure consistency. Adhere to predefined categories, naming conventions, and data fields for all assets. Standardisation will help generate error-free reports, ease search, and allow everyone to speak the same language when managing assets.
6. Track the Entire Asset Lifecycle
Be able to manage the entire life cycle of each asset registered. This includes when an asset was acquired, when it was deployed, when it is due for maintenance, when it is due to be retired, or when it is due to be disposed of. You can track the whole life cycle to help you plan when upgrades and replacements might be necessary and to make sure proper disposal methods are followed in accordance with environmental regulations.
Be able to manage the entire life cycle of each asset registered. This includes when an asset was acquired, when it was deployed, when it is due for maintenance, when it is due to be retired, or when it is due to be disposed of. You can track the whole life cycle to help you plan when upgrades and replacements might be necessary and to make sure proper disposal methods are followed in accordance with environmental regulations.
7. Integration into Other Systems
Integrate your IT asset register with other business systems to improve the efficiency and accuracy of data held within them, such as procurement, financial management, and helpdesk tools. This guarantees smooth data flow between systems and removes much of the necessity of manual data entry, thus allowing all departments to view real-time information.
Assign ownership of every asset to a user or a department. This builds responsibility among the users to care for the assets assigned to them. It also makes tracking more straightforward and ensures that in case of malfunction, all the problems are traced back to the assigned user.
9. Reporting and Analytics
This information can also be used with the reporting and analytics modules of your IT asset register to track asset performance, usage, and associated costs. Reports should be reviewed regularly for trends. This will enable the identification of underused assets, upcoming maintenance, or those reaching the end of their life cycle. Use the data to inform the decision-making process and thereby achieve optimised asset management.
10. Maintaining Licencing and Law Compliance
Keep records of software licensing compliance and adherence to regulatory requirements in your IT asset register. It should be updated at all times regarding software usage limitations and when the software license should be renewed to prevent non-compliance. Also, ensure that you keep up with regulations applicable to your business and check that your asset management conforms to the law.
11. Staff Education and Training
Provide users with training on the need for an IT asset register and ways of operating it efficiently. Ensure all users understand their role in asset management, from record-keeping updates to observing procedures for proper asset acquisition or retirement. This will help continuously update the register to be accurate and relevant.
As your organisation grows, so will your IT assets. Design for growth by selecting the tools and processes to support an increasing number of assets and users, and review these practices regularly to refine them so that they remain effective as your organisation evolves.
In a nutshell, the effectiveness of managing an IT asset register is based on a proper combination of accurate data entry, frequent audits, automation, and user accountability. Following these best practices will enable any organisation to ensure efficient management of its information technology assets by being secure and having everything to do with the general success of the business.
Bonus: An Overview of ICT Asset Management
In other words, ICT asset management can be described as a strategic approach to planning and managing organisational resources such as hardware, software, networks, and facilities infrastructure. The ultimate goal of ICT asset management is efficiency in executing business operations at the minimum cost and risk that these assets must yield. The effective management of ICT assets is very important in operational efficiency and innovation, as well as in supporting compliance with regulatory requirements.
Key Components of ICT Asset Management
These key components are what make ICT asset management necessary. Each contributes importantly to ensuring that ICT resources are optimised for use in the organisation while being in line with its goals.
Asset lifecycle management involves keeping records of the date of purchase, maintenance records, and disposal of all the ICT assets of the organisation, not necessarily in the form of hardware like computer machines and servers or networking equipment. Still, it includes software licenses, cloud services, and all forms of digital resources. More accurate inventory will bring a more reliable understanding of what is being owned, where it is, and how it is used.
Asset Lifecycle Management
An ICT asset goes through a lifecycle, from acquisition to eventual disposal. Lifecycle management tries to track down an ICT asset's stage in life, which includes deployment, utilisation, maintenance, upgrading, and retirement stages. Proper lifecycle management enables proper planning for the replacement of the assets and their full usage while ensuring their eventual disposal does not harm the environment.
Cost management is the second central element in managing ICT assets. It involves tracking the acquisition and ongoing maintenance costs of an asset, as well as eventual upgrades or replacements of cost. Understanding the total cost of an asset helps organisations make effective budgetary and resource supply decisions.
Licensing agreements and regulatory requirements are two significant concerns of software in ICT asset management, used by organisations in such a manner that ensures that organisations meet any required legal or regulatory obligation to secure data and privacy and to protect the environment. An opportunity is created through efficient and effective ICT assets to manage many legal issues and potential fines.
Performance Monitoring and Optimisation
Regular monitoring of ICT assets' performance needs to be performed to identify any underutilisation or overstrained resources. Performance data analysis can help organisations leverage their ICT infrastructure to an optimised extent with the help of resource re-allocation that can execute every system well. It helps in managing performance proactively so that downtime can be avoided and public productivity can be seen.
Asset tracking made easy.
Quite a number of ICT assets are employed as operation-support elements in business. For that reason, they may be a source of risk unless properly managed. Business risks emanating from the assets include asset failure, data breaches, and compliance violations. This risk is managed through the identification and mitigation of such asset-related risks. Implementation may include ensuring redundancy, conducting continual security audits, and full protection by all appropriate control measures.
Strategic Planning and Decision Making
ICT asset management is not only about asset tracking and maintenance but also a process related to strategic planning and decision-making. Data related to the usage and performance of the assets and their costs can inform decision-making for future investments in technology. The strategic approach ensures that the ICT resources support the eventual business goals towards success.
Benefits of Effective ICT Asset Management
When confidently deployed, ICT asset management has the following significant benefits for organisations:
- Cost Savings: Cost savings are a significant benefit to organisations, so this component will ensure expenditures are not necessary for the duplication of ICT hardware and software and maintenance. ICT asset optimisation would help organisations create a proper and effective budget and, therefore, allocate resources appropriately.
- Improved Efficiency: When ICT assets are well understood, resources are always used more efficiently. Downtime will be minimised, leading to a rise in productivity.
- Improved Security and Compliance: Proper management of ICT assets is more likely to give due credence to licensing agreements and regulatory provisions, hence lessening potential legal risks and chances of data leakage.
- Better Decision Making: With access to the information on ICT assets being correct and current, it becomes easier for the organisation to understand and make correct investment decisions in technology for its competitive survival in today's fast-moving digital world.
- Extended asset lifespan: Organisations can realise maximum life on their ICT assets by offering proper maintenance and performance monitoring.
Establish an ICT Asset Management System
Implementing an ICT asset register software will be pretty strategic; it must include starting with an entire inventory of all resources within the ICT domain. Any institution should set up transparent processes for following up, maintaining, and optimising the asset while having the right tools and software to support this action. With prudent regular audits, employee training, and interdepartmental cooperation, the success of ICT asset management is guaranteed.
Using itemit as Your IT Asset Register
itemit makes all of your processes quick and easy. You’ll be able to log, tag, track, and manage all of your IT assets in one place.
On top of this, itemit can also help you track your tools and equipment, inventory lists, and any other technology that needs additional accountability. You can track all of these separately or in tandem with our IT asset register software, which we can provide for your needs.
To find out more about how itemit can help, either fill in the form below or drop us an email at team@itemit.com.