Stay updated on the latest trends and innovations in modern construction, building methods, and advanced technologies transforming the industry today and beyond.
Radio frequency identification technology has changed how organizations monitor and control their physical assets. Traditional tracking methods depend on manual processes or direct scanning, but RFID systems provide clearer visibility into asset location, usage patterns, and operational status. The technology converts complicated inventory challenges into streamlined management processes that produce concrete results. Businesses today experience mounting pressure to improve resource utilization while maintaining operational standards through informed decision making.

Understanding RFID Technology Fundamentals
Radio frequency identification tracking represents an evolution in asset monitoring systems. Working on principles similar to barcode technology, RFID tags communicate wirelessly with scanning devices through electromagnetic fields. Each tag contains a microchip and antenna that transmit unique identification data when activated by a reader.
RFID's strength comes from its contactless operation. Barcodes require direct visual scanning, but RFID tags can be read through various materials and from distances up to several meters. This means you can identify assets stored behind other items, embedded within equipment, or located in difficult positions without physical handling.
Each tag emits a distinct frequency that allows immediate identification once within scanner range. This happens instantly, enabling quick inventory counts and location updates. Advanced RFID tracking apps connect this hardware capability with user-friendly software interfaces, creating thorough asset management systems.
The technology operates across different frequency ranges, each suited to specific applications:
- Low-frequency systems excel in environments with metal interference and liquid presence
- High-frequency options provide balanced performance for most indoor applications
- Ultra-high frequency systems deliver extended read ranges ideal for warehouse operations
- Microwave frequencies support specialized applications requiring maximum range
Choosing the appropriate frequency depends on your specific operational requirements and environmental conditions. Professional RFID asset tracking explained guidance helps organizations select optimal configurations for their unique circumstances.
Comprehensive Asset Tracking Strategies
Track Every Asset in Your Organization
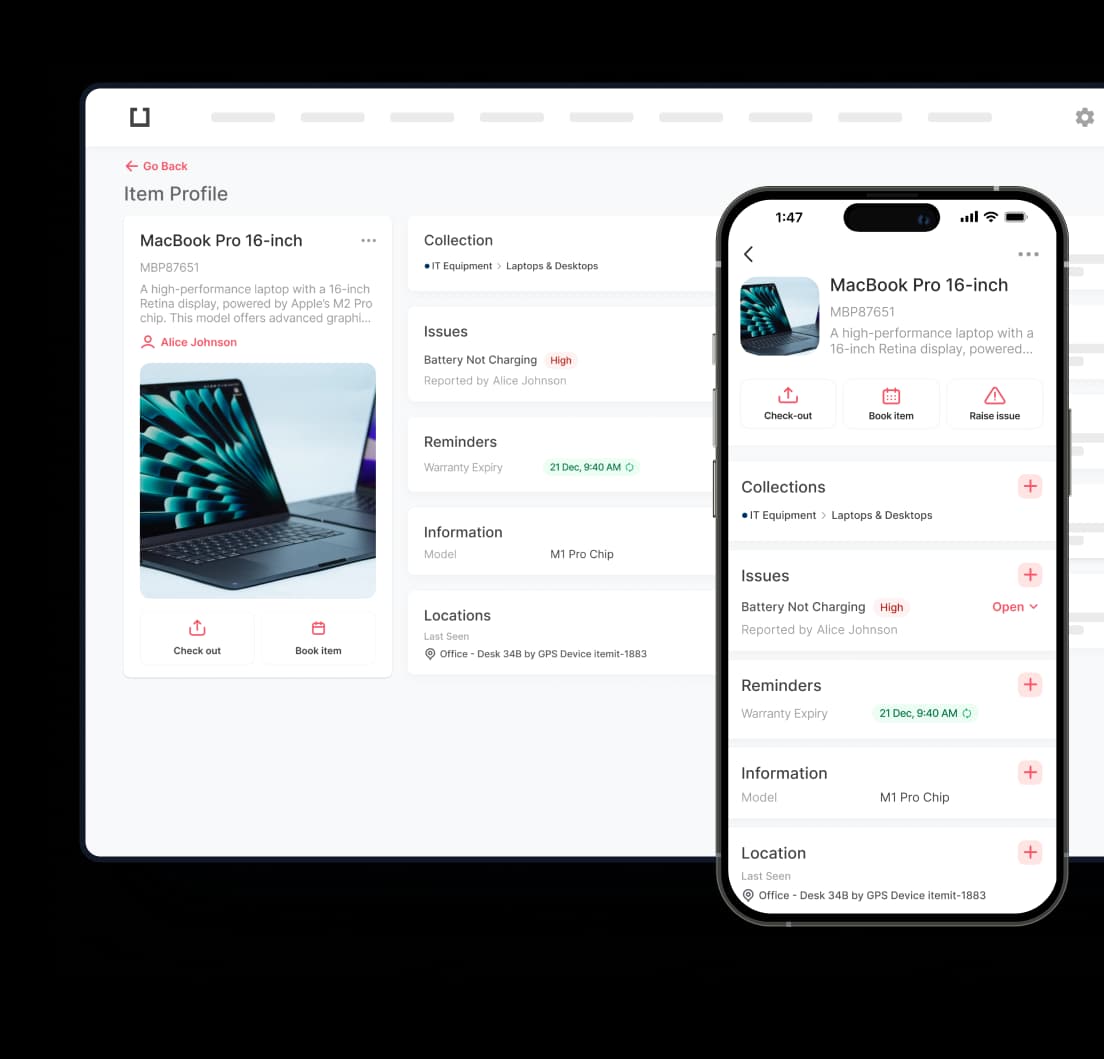
Start your smart RFID implementation by tracking every single asset within your organization. Don't make the mistake of partial tracking—this creates information gaps that hurt operational visibility and decision-making accuracy. Complete asset coverage builds the foundation for understanding resource utilization patterns and spotting optimization opportunities.
Your RFID tracking app should handle different asset categories, from expensive machinery to everyday supplies. Each asset type needs specific data fields and monitoring parameters. Manufacturing equipment might need maintenance schedules and usage hours, while office supplies require quantity tracking and reorder thresholds.
Implement Tiered Tracking Levels
Think about setting up tiered tracking levels based on asset value and importance. Expensive equipment deserves detailed monitoring with frequent status updates, while cheaper items might need basic location and quantity tracking. This approach balances complete coverage with system efficiency.
Set up real time asset tracking capabilities to enable immediate response to changing conditions. When assets move unexpectedly or exceed predetermined usage thresholds, automated alerts ensure prompt attention. This quick response prevents minor issues from becoming operational disruptions.
Transportation and Logistics
Getting materials from suppliers to jobsites presents logistical puzzles. Urban sites might have limited access, requiring smaller trucks and more frequent deliveries. Remote projects need careful coordination to avoid costly return trips.
Supply chain materials management becomes critical when projects span multiple locations or phases. A project manager might coordinate deliveries to three buildings while tracking materials in transit, in storage, and installed. Weather adds another variable—rainy seasons require covered storage, and extreme temperatures affect concrete mix designs and adhesive curing.
Go Beyond Basic Location Tracking
Don't limit your data collection to simple location tracking. Current systems can capture usage patterns, maintenance histories, and performance metrics. This information shows trends that inform strategic decisions about asset replacement, capacity planning, and resource allocation. The more thorough your tracking approach, the richer your operational insights become.
Use Multiple Devices to Track Your Assets
Make Your RFID System Accessible Everywhere
Set up your RFID tracking system to work across multiple locations and devices. Your tracking app should work smoothly whether accessed through smartphones, tablets, desktop computers, or specialized handheld scanners. This multi-platform approach ensures information accessibility regardless of user location or preferred device.
Leverage Mobile Capabilities for Field Operations
Take advantage of mobile capabilities for field operations and distributed workforces. Train maintenance technicians to update asset status while performing repairs, have warehouse staff conduct inventory counts while moving around, and enable managers to access real-time reports during site visits. The portability eliminates delays between asset interactions and data updates.
Implement Cloud-Based Data Synchronization
Use cloud-based architectures to enable synchronized data access across all connected devices. Changes made on one platform should immediately show up across the entire system, maintaining data consistency and preventing conflicts. This synchronization proves critical when multiple team members interact with the same assets at once.
Design Responsive User Interfaces
Make sure your user interface design adapts to different screen sizes and input methods. Desktop interfaces can handle detailed asset profiles and complex reporting features, while mobile versions should prioritize quick actions and display of necessary information. Responsive design ensures optimal functionality regardless of access method.
Set Up Role-Based Security Controls
Establish role-based permissions to control what information different users can view and modify. Field technicians might access basic asset information and status updates, while managers enjoy full reporting and configuration capabilities. These controls protect sensitive data while maintaining operational efficiency.

Create Data and Export Your Reports
Turn Every Interaction into Valuable Data
Make every interaction with your RFID system count by generating valuable data that shows operational patterns and improvement opportunities. Asset check-outs, location changes, maintenance activities, and usage tracking create detailed audit trails that support both operational management and strategic planning initiatives.
Eliminate Manual Recording Errors
Replace manual recording with automated data collection to eliminate errors while providing unprecedented detail about asset utilization. Traditional tracking methods depend on periodic manual updates that often miss critical information. RFID systems capture every significant event, creating complete operational histories for each tracked asset.
Choose Apps with Thorough Reporting Capabilities
Select an RFID tracking app that turns raw data into actionable insights through thorough reporting capabilities:
Standard Reporting Features:
- Asset utilization rates and productivity metrics
- Maintenance schedules and compliance tracking
- Location histories and movement patterns
- Cost allocation and departmental usage
- Inventory levels and reorder notifications
- User activity logs and access records
Set Up Custom Reporting Functions
Configure custom reporting functionality to address specific analytical requirements unique to your operations. Enable export capabilities for integration with existing business systems and external analysis tools. PDF reports provide professional documentation for stakeholder presentations, while CSV exports support detailed analysis in spreadsheet applications.
Integrate with Supply Chain Systems
Connect your supply chain automation with thorough RFID data integration. Make tracking information flow smoothly between inventory management, procurement, and financial systems, eliminating manual data entry and reducing processing delays. This integration creates end-to-end visibility that supports strategic supply chain optimization.
Establish Regular Reporting Schedules
Set up regular reporting schedules to ensure stakeholders receive timely information for decision-making. Use automated report generation and distribution to eliminate administrative overhead while maintaining consistent communication. Configure exception reports to highlight assets requiring immediate attention, enabling proactive management of potential issues.
Advanced Implementation Strategies
Smart RFID for small business implementations need careful planning and phased rollouts. Starting with expensive or frequently used assets provides immediate benefits while allowing teams to develop system expertise. This approach reduces implementation risks while demonstrating value to stakeholders.
Integration planning should consider existing business systems and workflows. RFID data becomes most valuable when connected to procurement, accounting, and production management systems. These connections eliminate duplicate data entry while providing thorough operational visibility.
User training programs ensure successful adoption across all organizational levels. Different user groups need tailored training approaches that address their specific responsibilities and system interactions. Ongoing support and refresher training help maintain system effectiveness as personnel changes occur.
Change management strategies address cultural shifts that come with new tracking systems. Some employees might initially resist increased visibility into their asset usage patterns. Clear communication about system benefits and appropriate privacy protections helps overcome resistance while encouraging adoption.
Performance monitoring tracks system effectiveness and identifies optimization opportunities. Key metrics might include data accuracy rates, user adoption levels, and operational efficiency improvements. Regular assessment ensures the system continues meeting organizational needs as requirements evolve.
Following established RFID best practices during deployment accelerates success rates and minimizes common implementation pitfalls. These proven methodologies help organizations avoid costly mistakes while maximizing system effectiveness from day one.

Technology Evolution and Future Considerations
RFID technology keeps advancing with improved read ranges, enhanced data storage capabilities, and better integration options. Battery-powered tags now offer extended operational life and greater functionality, while passive tags become smaller and more cost-effective.
Internet of Things integration expands RFID capabilities beyond simple identification. Smart tags can monitor environmental conditions, track usage intensity, and communicate directly with maintenance systems. These capabilities transform basic tracking into thorough asset intelligence platforms.
Artificial intelligence applications enhance RFID data analysis through predictive analytics and pattern recognition. Machine learning algorithms identify optimization opportunities that might escape human analysis. These insights support strategic decision-making about asset allocation, replacement timing, and operational improvements.
Cloud computing advances enable more sophisticated RFID implementations with reduced infrastructure requirements. Software-as-a-Service models provide enterprise-grade functionality without significant capital investments. These platforms offer scalability that grows with organizational needs.
Security enhancements address concerns about unauthorized data access and tag cloning. Advanced encryption and authentication protocols protect sensitive asset information while maintaining operational efficiency. Regular security updates ensure ongoing protection against emerging threats.
Maximizing Return on Investment
Effective RFID inventory management delivers measurable benefits across multiple operational areas. Reduced inventory carrying costs result from improved accuracy and optimized stock levels. Labor savings emerge from automated data collection and streamlined asset location processes.
Asset utilization improvements generate significant value through better resource allocation and reduced idle time. RFID visibility enables organizations to share assets across departments and projects more effectively. This optimization reduces equipment purchase requirements while maintaining operational capacity.
Key ROI Drivers:
- Inventory accuracy improvements reducing carrying costs and stockouts
- Labor efficiency gains from automated data collection processes
- Asset utilization optimization maximizing return on equipment investments
- Maintenance cost reductions through predictive scheduling strategies
- Compliance automation eliminating manual documentation overhead
- Loss prevention benefits from real-time location monitoring
Compliance documentation becomes automatic with thorough RFID tracking. Regulatory requirements for asset maintenance, calibration, and inspection receive smooth support through automated record-keeping. This capability reduces compliance costs while minimizing audit risks.
Loss prevention benefits from immediate visibility into asset movements and locations. Unauthorized asset removal triggers immediate alerts that enable rapid response. Historical tracking data supports investigation activities when assets go missing.
The combination of operational efficiency, cost reduction, and strategic insights creates compelling returns on RFID investments. Organizations typically recover implementation costs within months while enjoying ongoing benefits for years. This value proposition makes RFID tracking an attractive investment for organizations seeking competitive advantages through operational excellence.
Success with RFID asset tracking needs selecting systems that align with organizational needs while providing room for future growth. Thorough platforms deliver the visibility and control necessary for current asset management challenges. The technology transforms traditional reactive approaches into proactive strategies that drive operational excellence and competitive advantage.


Modern Methods of Building Construction. Trends and Innovations to Watch

How to Create an Effective Construction Management Plan for Your Project
Create an effective construction management plan that improves safety, minimises delays and keeps your project organised and on track from planning to completion.

A Complete Guide to Construction Cost Management and Planning
Effective construction cost management and planning improve profitability, enhance financial stability, and strengthen resource allocation across every project.