Stay updated on the latest trends and innovations in modern construction, building methods, and advanced technologies transforming the industry today and beyond.
Effective equipment tracking has become a cornerstone of modern business operations, yet many organisations still struggle with outdated manual processes and spreadsheet-based systems. RFID equipment tracking represents a transformative solution that addresses these challenges through intelligent automation and real-time data collection.

Key Takeaways
- RFID equipment tracking uses radio frequency identification technology to automatically monitor and locate business assets without requiring line-of-sight scanning
- Real-time visibility enables organisations to achieve up to 95% inventory accuracy whilst reducing manual tracking time by 80-95%
- Automated inventory systems eliminate human error and provide instant data updates, improving operational efficiency across multiple industries
- Equipment monitoring systems offer scalable solutions that grow with your business, from small offices to large industrial facilities
Understanding RFID Equipment Tracking Technology
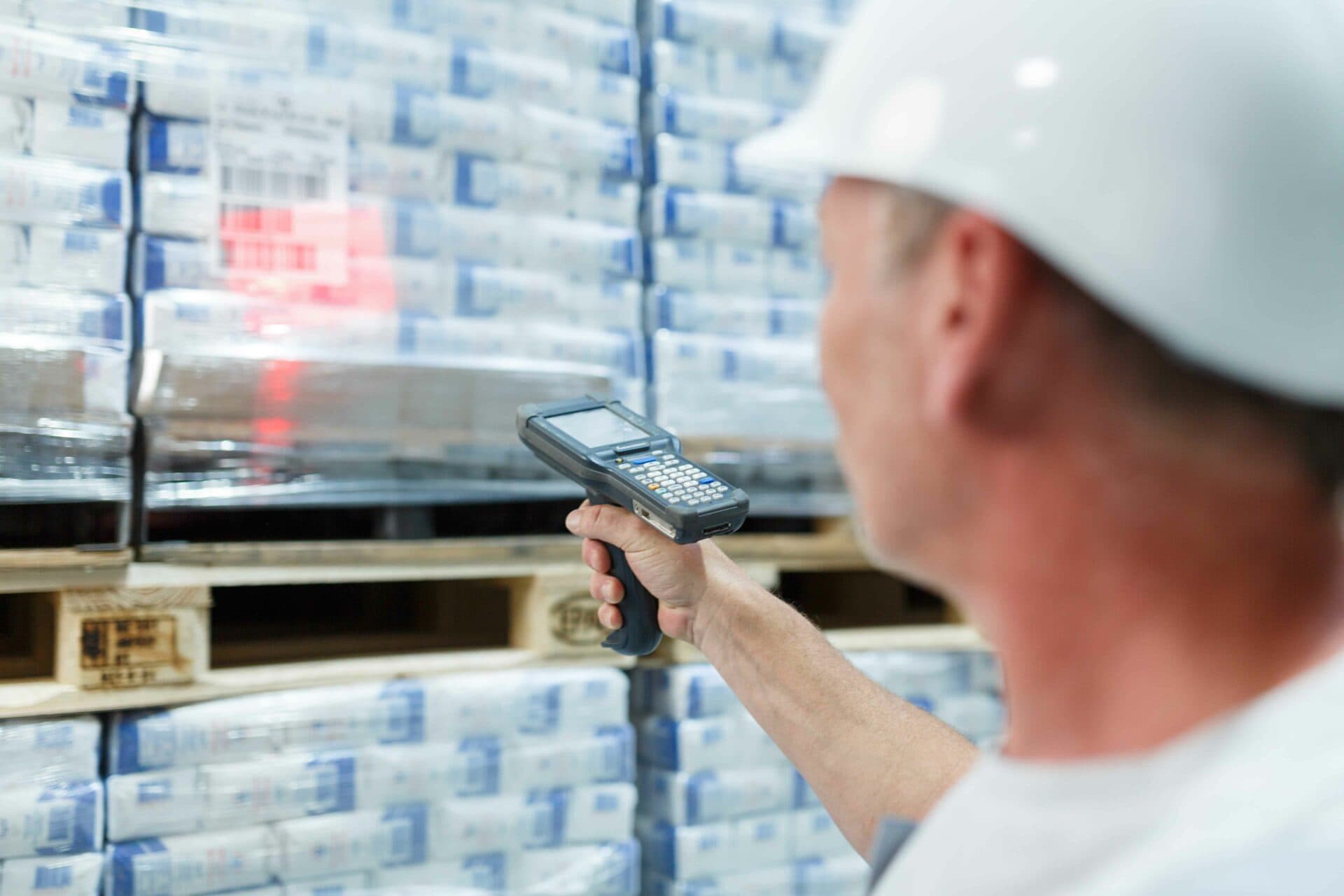
RFID (Radio Frequency Identification) technology operates through electromagnetic fields to automatically identify and track tags attached to objects. Unlike traditional barcode systems, an rfid equipment tracking system doesn't require direct line-of-sight scanning, making it exceptionally efficient for bulk asset identification.
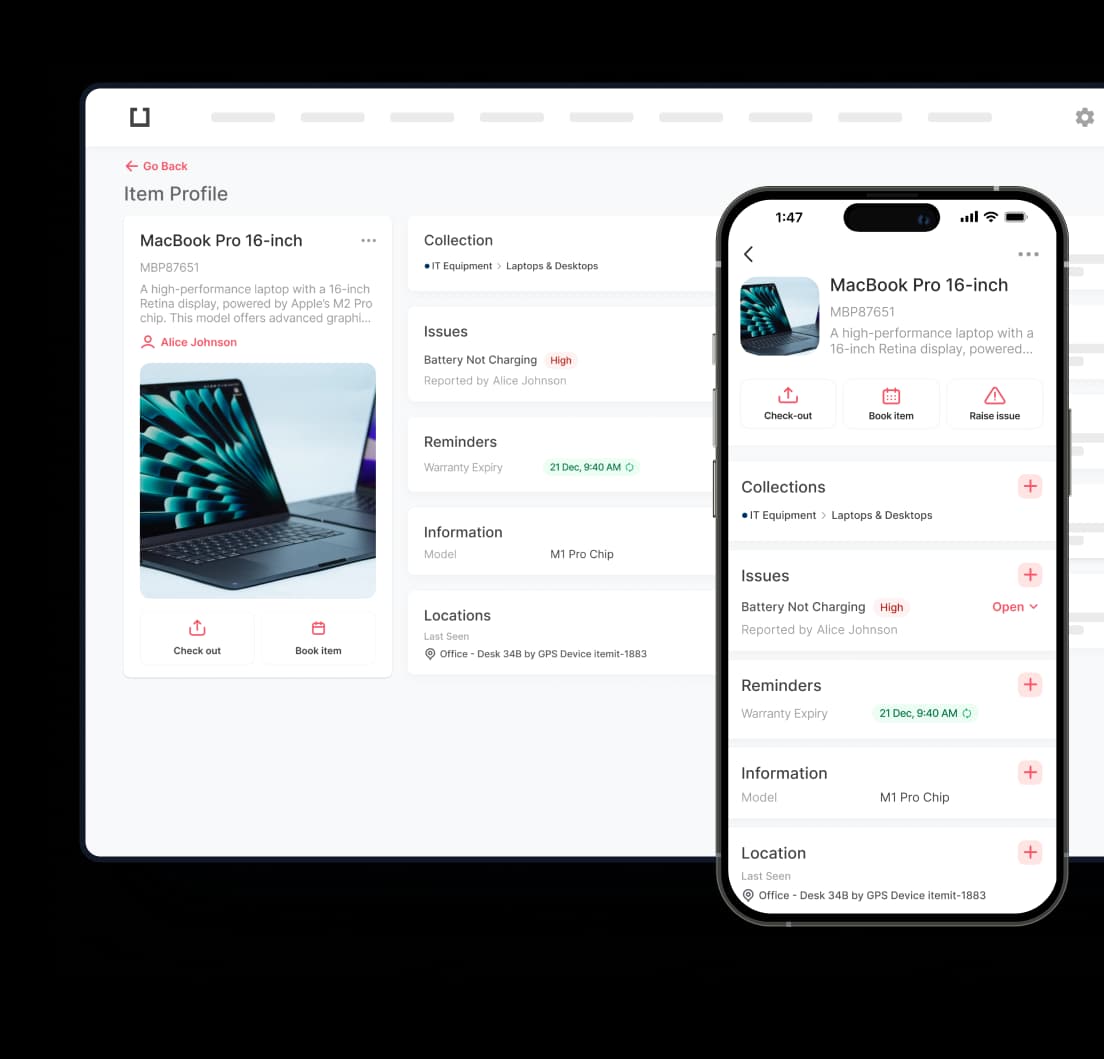
The technology consists of three fundamental components: RFID tags containing electronic data, readers that capture tag information, and software platforms that process and manage the collected data. When a reader detects a nearby tag, it wirelessly retrieves the stored information and transmits it to your central management system.
The Three Types of RFID Tags
Active RFID tags contain internal batteries and can transmit signals over distances up to 150 metres. These are ideal for tracking high-value equipment across large facilities or outdoor environments. The battery life typically ranges from three to five years, providing consistent performance for long-term asset monitoring.
Passive RFID tags derive power from the reader's radio waves and offer a cost-effective solution for most business applications. With no internal battery, they have unlimited lifespan and are perfect for tracking items that don't move frequently or require constant monitoring.
Semi-passive tags combine the best of both worlds, featuring internal batteries for extended functionality whilst maintaining the power-efficient design of passive systems. These are particularly useful for monitoring environmental conditions alongside location data.
Implementing Your Automated Inventory System
The transition to an automated inventory system requires strategic planning and phased implementation. Begin by conducting a comprehensive audit of your current assets and identifying specific tracking requirements. This foundation ensures your RFID solution aligns with operational needs and delivers measurable returns.
Phase One: Pilot Programme
Start small by selecting a specific department or asset category for initial implementation. This approach allows you to test system functionality, refine processes, and demonstrate value before organisation-wide deployment. Choose assets that are frequently moved or have high replacement costs to maximise pilot programme impact.
Phase Two: System Integration
Modern rfid equipment tracking system solutions must integrate seamlessly with existing business software. Your chosen platform should connect with ERP systems, maintenance management software, and financial applications to create a unified data environment. This integration eliminates data silos and provides comprehensive asset visibility across all business functions.
Phase Three: Full Deployment
Once pilot results demonstrate clear benefits, expand the system to encompass all relevant assets and locations. This phase requires comprehensive staff training, workflow adjustments, and continuous monitoring to ensure optimal performance.

Benefits of Modern Equipment Monitoring Systems
Equipment monitoring systems powered by RFID technology deliver substantial operational improvements that extend far beyond simple location tracking. The real-time data collection capabilities transform how organisations manage their physical assets.
Enhanced Asset Utilisation
Real-time tracking reveals equipment usage patterns, enabling better resource allocation and utilisation optimisation. You can identify underused assets, redistribute equipment across departments, and make informed purchasing decisions based on actual demand rather than guesswork.
Preventive Maintenance Excellence
RFID tags can store maintenance histories, service schedules, and condition monitoring data directly on the equipment. This information enables proactive maintenance planning, reduces unexpected breakdowns, and extends equipment lifespan through proper care scheduling. Healthcare facilities particularly benefit from this approach to Track Healthcare Equipment, ensuring life-critical devices remain operational and properly maintained.
Theft Prevention and Recovery
Visible RFID tags serve as theft deterrents whilst providing recovery capabilities if assets go missing. The system maintains detailed logs of who accessed which equipment and when, creating accountability and reducing losses through improved oversight. This proves particularly valuable when organisations need to Track High-Value Assets such as servers, specialised machinery, or expensive instruments where security monitoring is paramount.
Overcoming Implementation Challenges
Whilst RFID technology offers significant advantages, successful implementation requires addressing potential obstacles. Understanding these challenges enables better planning and smoother transitions.
Environmental Considerations
Metal surfaces, liquids, and electromagnetic interference can affect RFID performance. However, advances in tag design and reader technology have largely mitigated these issues. Working with experienced providers ensures proper tag selection and placement for optimal performance in challenging environments. Outdoor operations, such as those requiring comprehensive Agricultural Asset Management, benefit from ruggedised tags designed to withstand harsh weather conditions and extended exposure to natural elements.
Cost Management
Initial investment costs remain a primary concern for many organisations. However, businesses typically achieve positive returns within 12-24 months through reduced labour costs, improved accuracy, and decreased asset losses. The key is conducting thorough cost-benefit analysis to demonstrate long-term value.
Staff Training and Change Management
Employee resistance to new technology can hinder implementation success. Address concerns through transparent communication about benefits, job security, and career development opportunities. Comprehensive training programmes ensure staff feel confident using new systems and understand how RFID improves their daily work.
Selecting the Right Solution
Choosing appropriate RFID solutions requires evaluating multiple factors including system scalability, integration capabilities, and ongoing support requirements. Consider providers with proven experience in your industry who understand specific operational challenges and compliance requirements.
Software Platform Considerations
Your chosen platform should offer intuitive interfaces, robust reporting capabilities, and flexible customisation options. Cloud-based solutions provide accessibility advantages, whilst on-premise systems may better serve organisations with strict data governance requirements.
Hardware Selection
Reader and tag selection depends on environmental conditions, tracking range requirements, and budget constraints. Fixed readers work well for monitoring specific checkpoints, whilst handheld devices offer flexibility for ad-hoc scanning and inventory audits.
Support and Training
Ongoing support from your RFID provider ensures system optimisation and troubleshooting assistance. Look for companies offering comprehensive training programmes, technical documentation, and responsive customer service.

Maximising Return on Investment
RFID equipment tracking systems deliver measurable financial returns through multiple channels. Labour cost reductions represent the most immediate benefit, as automated tracking eliminates manual counting and searching activities.
Improved accuracy prevents costly ordering mistakes and stockout situations that disrupt operations. Enhanced asset utilisation means getting maximum value from existing equipment rather than purchasing unnecessary replacements.
Detailed Cost Analysis and ROI Projections
Understanding the financial implications of rfid equipment tracking implementation helps justify initial investment and set realistic expectations. Small to medium businesses typically invest £15,000-£50,000 for comprehensive systems, whilst larger enterprises may require £100,000+ depending on asset volume and complexity.
Consider a manufacturing facility tracking 5,000 pieces of equipment. Manual inventory processes requiring 40 hours monthly at £25 per hour cost £12,000 annually in labour alone. An automated inventory system reduces this to 8 hours monthly, saving £9,600 yearly whilst improving accuracy from 75% to 95%.
Asset loss prevention adds significant value. Companies losing £50,000 annually in misplaced or stolen equipment can reduce losses by 80-90% through RFID implementation. Combined with maintenance optimisation benefits—preventing one major equipment failure worth £100,000 through predictive maintenance—the business case becomes compelling.
Insurance premiums often decrease when companies demonstrate improved asset security and maintenance practices through comprehensive equipment monitoring systems. Some insurers offer 10-15% reductions for organisations with verified RFID tracking capabilities.
Measuring Success
Establish key performance indicators before implementation to track system effectiveness. Common metrics include inventory accuracy percentages, time saved on asset-related tasks, and reduction in equipment losses. Regular performance reviews ensure the system continues delivering expected benefits.
Continuous Improvement
Modern RFID systems generate valuable data analytics that reveal operational insights. Use this information to optimise workflows, identify training needs, and make strategic decisions about future equipment investments.
Future-Proofing Your Investment
RFID technology continues evolving with advances in Internet of Things (IoT) integration, artificial intelligence, and sensor capabilities. Choose solutions that can accommodate future enhancements without requiring complete system replacement.
Battery-free sensors, improved read ranges, and enhanced data processing capabilities will further expand RFID applications. Your selected platform should support these innovations through regular updates and modular architecture.
Integration with Emerging Technologies
Modern rfid equipment tracking system platforms increasingly integrate with artificial intelligence and machine learning algorithms to provide predictive analytics. These systems analyse usage patterns, maintenance histories, and environmental data to forecast equipment failures before they occur.
Blockchain integration offers enhanced security and audit trails, particularly valuable for regulated industries requiring immutable tracking records. Smart contracts can automatically trigger maintenance requests or reorder supplies when RFID data indicates specific thresholds.
5G connectivity enables faster data transmission and supports real-time tracking of mobile assets across vast geographical areas. This advancement particularly benefits construction companies, logistics providers, and field service organisations managing distributed equipment fleets.
Edge computing capabilities allow local data processing, reducing latency and enabling automated inventory system functionality even during network connectivity interruptions. This resilience proves crucial for mission-critical operations that cannot afford tracking system downtime.
Integration with augmented reality (AR) applications helps technicians quickly locate specific equipment and access maintenance instructions through visual overlays. This technology bridges physical and digital asset management, improving field service efficiency and reducing training requirements for complex equipment maintenance procedures.

Getting Started
Beginning your RFID journey requires careful planning and realistic expectations. Start by documenting current asset management challenges, setting specific improvement goals, and researching potential solution providers. Selecting the right rfid asset tracking software forms the foundation of successful implementation, as the platform will determine long-term scalability and integration capabilities.
Consider engaging consultants or conducting pilot programmes to validate assumptions and refine requirements. This preparation ensures your final system selection aligns with operational needs and delivers expected benefits.
The transformation from manual asset tracking to automated RFID systems represents a significant operational advancement. With proper planning, appropriate technology selection, and comprehensive implementation support, organisations can achieve remarkable improvements in efficiency, accuracy, and overall asset management effectiveness.
Frequently Asked Questions
What's the difference between RFID equipment tracking and barcode systems?
RFID systems read multiple tags simultaneously without requiring line-of-sight, whilst barcodes need individual scanning and direct visibility.
How long do RFID tags last on equipment?
Passive RFID tags have no expiry date and can last indefinitely, whilst active tags typically provide 3-5 years of battery life.
Can RFID tags work on metal equipment?
Yes, specially designed on-metal RFID tags are available that perform excellently on metallic surfaces and equipment.
What's the typical return on investment for RFID systems?
Most businesses achieve positive ROI within 12-24 months through reduced labour costs, improved accuracy, and decreased asset losses.
Do RFID systems require internet connectivity?
Basic RFID functionality works offline, but cloud-based features and real-time updates require internet connectivity for optimal performance.
How secure is RFID data transmission?
Modern RFID systems include encryption and authentication protocols to protect data transmission and prevent unauthorised access
What training is required for staff to use RFID systems?
Most RFID systems are intuitive and require minimal training, typically just a few hours to understand basic scanning and data entry procedures.


Modern Methods of Building Construction. Trends and Innovations to Watch

How to Create an Effective Construction Management Plan for Your Project
Create an effective construction management plan that improves safety, minimises delays and keeps your project organised and on track from planning to completion.

A Complete Guide to Construction Cost Management and Planning
Effective construction cost management and planning improve profitability, enhance financial stability, and strengthen resource allocation across every project.