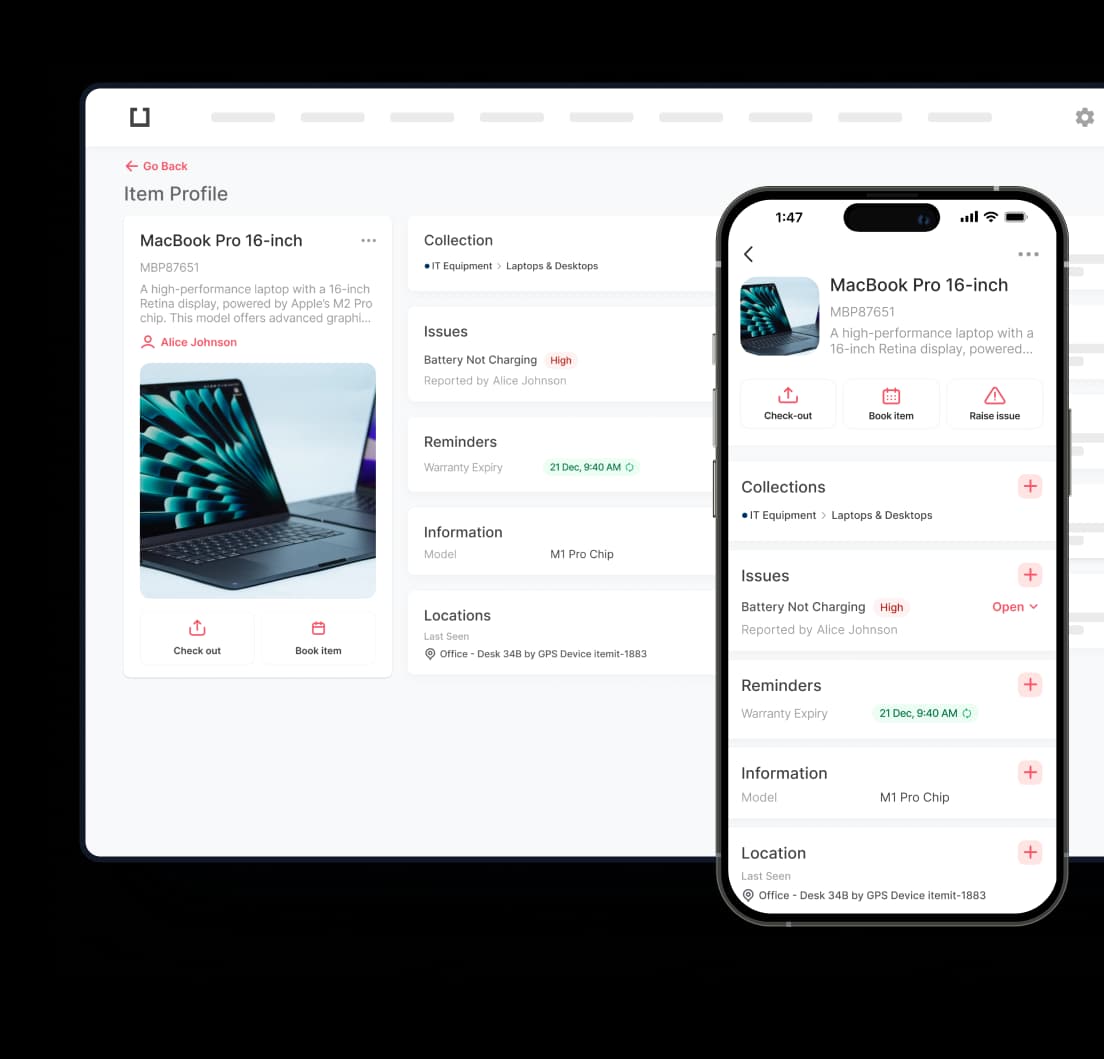
Success or failure in today's competitive business landscape often hinges on how effectively a company monitors and controls its assets and stock. Quietly powering many of the most effective tracking operations is the unassuming 2D barcode – a technology that seldom receives the recognition it deserves. These square-patterned data carriers represent a quantum leap beyond conventional linear barcodes. With their ability to pack extensive information into remarkably compact spaces, these versatile two-dimensional barcodes have fundamentally transformed operational processes across industries – from warehouse management to point-of-sale interactions and from field service tracking to customer engagement.
What Are 2D Barcodes?
A 2D barcode stores information in both horizontal and vertical patterns—that's where the term 2 dimensional barcode comes from. Traditional linear barcodes (the familiar zebra-striped pattern) only hold about 20-25 characters, but their more advanced 2D cousins pack hundreds or thousands of characters into a similarly sized space.
What are 2D barcodes capable of storing? These compact data powerhouses can contain:
- Plain text information
- Web addresses and URLs
- Complete contact details
- Serial and tracking numbers
- Detailed product specifications
- Equipment maintenance histories
- Precise location coordinates
This extensive data capacity makes 2D barcodes particularly valuable for businesses managing assets and inventory at scale.
Barcode Origins and Evolution
Barcodes have a longer history than many realize. Norman Joseph Woodland and Bernard Silver filed the first patent for a barcode-type system back in 1949, though it looked quite different from today's versions. The familiar UPC (Universal Product Code) that transformed retail was invented in the early 1970s, with its first commercial use scanning a pack of Wrigley's gum in 1974.
The jump to 2D barcodes happened later. Symbol Technologies developed the first true 2D barcode—PDF417—in 1991. Then, in 1994, Denso Wave created QR codes in Japan to track automotive parts during manufacturing.
When was barcode technology widely adopted beyond retail scanning? The smartphone boom of the late 2000s changed everything, essentially putting a barcode scanner in millions of pockets worldwide.
Types of 2D Barcodes
While QR codes dominate public awareness, the 2D barcode family includes several distinct formats with unique strengths:
1. QR (Quick Response) Codes:
- Capacity: Up to 7,089 numeric or 4,296 alphanumeric characters
- Distinctive Feature: Three-position detection patterns in corners
- Best For: Consumer-facing applications, marketing, payments
- Error Correction: Can restore up to 30% of damaged data
- Scanning Speed: Extremely fast (hence "Quick Response")
- Mobile Compatibility: Excellent native support on most smartphones
2. Data Matrix:
- Capacity: Up to 2,335 alphanumeric characters
- Distinctive Feature: Square or rectangular grid with finder pattern
- Best For: Marking small components, medical devices, electronic components
- Error Correction: Reed-Solomon algorithm allows reading even when 20-30% damaged
- Size Advantage: Can be printed extremely small (as tiny as 2×2 mm)
- Industry Adoption: Aerospace, defense, electronics manufacturing
3. Aztec Code:
- Capacity: Up to 3,832 numeric or 3,067 alphanumeric characters
- Distinctive Feature: Square bullseye pattern at center
- Best For: Transportation tickets, boarding passes, ID verification
- Error Correction: Adjustable levels from 5% to 95%
- Scanning Benefit: No quiet zone required around the symbol
- Standards: ISO/IEC 24778 compliant for global use
4. PDF417:
- Capacity: Up to 1,800 characters
- Distinctive Feature: Stacked linear barcode resembling a pile of 1D codes
- Best For: ID cards, driver's licenses, inventory management
- Error Correction: Nine levels available depending on security needs
- Format Type: Technically a "stacked linear" rather than matrix code
- Government Use: Common on government-issued identification documents
5. MaxiCode:
- Capacity: Up to 93 characters, optimized for shipping information
- Distinctive Feature: Hexagonal grid with bullseye center
- Best For: High-speed sorting and tracking of packages
- Creator: Developed by UPS for their shipping operations
- Scanning Benefit: Designed for ultra-high-speed conveyor scanning
- Industry Standard: Used globally in logistics and shipping
Understanding these distinct formats helps businesses select the optimal 2D barcode type for specific operational needs rather than defaulting to the most familiar option. The right selection can dramatically improve scanning reliability, data security, and overall system efficiency.
2D Barcode vs QR Code: Important Distinctions
Understanding these distinct formats helps businesses select the optimal 2D barcode type for specific operational needs rather than defaulting to the most familiar option. The right selection can dramatically improve scanning reliability, data security, and overall system efficiency.

People often use "QR code" and "2D barcode" as synonyms, but that's not technically correct. The relationship in the 2D barcode vs. QR code comparison is category versus specific type—QR codes are just one format within the broader 2D barcode family.
Key differences to understand about 2D barcode vs QR code:
- Classification: The term "2D barcode" covers many formats (QR, Data Matrix, Aztec, etc.), while "QR code" means one format.
- Visual Design: QR codes feature distinctive square finder patterns in three corners; other 2D barcodes use different identifying markers.
- Data Storage: Some 2D barcode types exceed QR codes in storage capacity, while others optimize for specific data types.
- Best Uses: QR codes typically work better for consumer-facing applications, but other 2D barcode formats often prove superior for industrial or specialized tasks.
This distinction matters because defaulting to QR codes without considering alternatives might mean missing out on a format better suited to your specific requirements.
How 2D Barcodes Improve Business Operations
Implementing 2D barcodes as part of your asset-tracking solution delivers measurable improvements across multiple operational areas:
Enhanced Data Management
Rich Data Encoding
- Store complete asset profiles (150+ characters) directly in a single code
- Include maintenance histories, ownership records, and technical specifications
- Encode URLs that link to cloud-based asset records for unlimited information
- Embed serialization data that uniquely identifies each item
Damage-Tolerant Information
- Maintain readability even when 30% of the code is damaged or obscured
- Continue functioning in harsh environments with dirt, scratches, or partial damage
- Reduce replacement costs for labels in high-wear locations
- Ensure critical data remains accessible during emergency situations
Operational Efficiency Gains
Space Optimization
- Fit complete data into 1/10th the space of traditional barcodes
- Apply functional codes to small components previously too tiny to tag
- Reduce label size by up to 80% while increasing data capacity
- Maintain brand aesthetics with smaller, less obtrusive tracking codes
Scanning Improvements
- Reduce scanning time by 60-70% with omnidirectional reading capability
- Eliminate alignment issues that plague traditional barcode systems
- Enable scanning from distances up to 3x greater than 1D codes
- Function effectively in low-light environments where 1D codes fail
Cost-Effective Implementation
Technology Investment Comparison
- Implement at 15-25% the cost of comparable RFID systems
- Create new codes with standard printers rather than specialized equipment
- Eliminate ongoing tag costs through digital distribution of codes
- Leverage existing smartphones instead of purchasing dedicated scanners
Maintenance Economies
- Reduce label replacement frequency by up to 60% through better durability
- Decrease scanning errors by 70-80%, cutting exception-handling labor costs
- Lower training requirements through intuitive scanning processes
- Minimize database storage requirements through compressed data formats