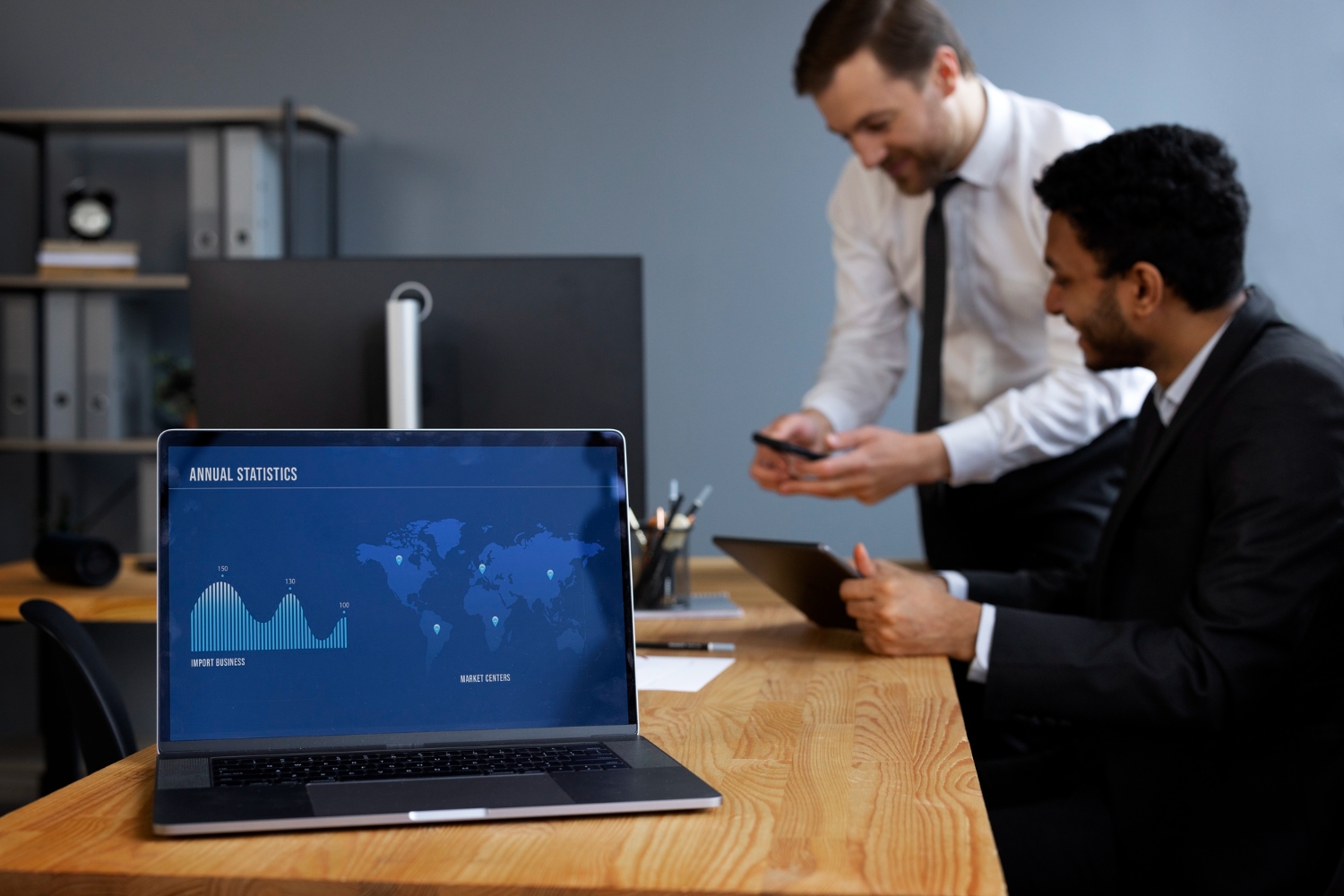

How To Undertake An Effective IT Asset Audit

Maintaining precise oversight of your technology inventory is essential for maximising operational efficiency. When you’ve established comprehensive control over your IT ecosystem, productivity naturally follows. While gaining this control might initially appear challenging, specialised IT asset audit solutions make this process remarkably straightforward. Using the right tools makes conducting extensive audits not only feasible but also simplified. Let’s look at the principles of inventory auditing and its crucial importance to your company.
Understanding IT Asset Management Audits
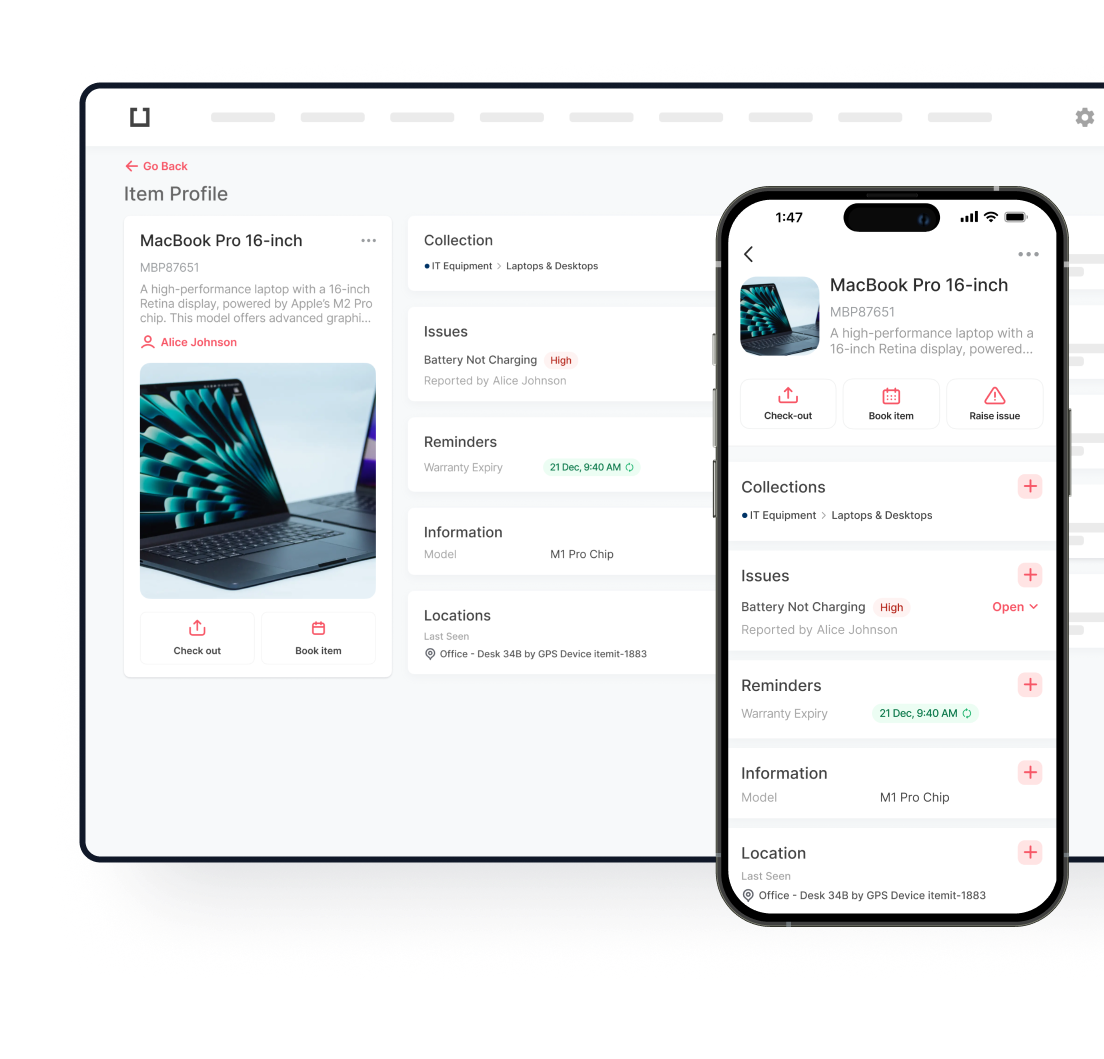
An IT asset management audit provides a comprehensive overview of your organisation’s technology resources, including all software applications, hardware devices, and peripheral equipment. These audits expose exact asset quantities, locations, operational status, and physical condition going beyond basic calculations.
Key components typically covered in an IT hardware audit include:
- Software assets: Operating systems, application licenses, proprietary programs
- Hardware elements: Workstations, servers, network equipment, mobile devices
- Peripheral components: Connectivity cables, adapters, power supplies, specialised accessories
- Digital services: Cloud subscriptions, SaaS applications, virtual resources
Tracking these diverse elements might seem overwhelming without proper systems in place. However, implementing specialised inventory audit app solutions transforms this challenge into a manageable process. When leveraging digital tracking systems, on-site IT inventory audits become remarkably efficient. These platforms provide immediate visibility into asset allocation, condition assessment, and valuation metrics—substantially simplifying the entire audit workflow.
The Critical Importance of Regular Hardware Software Inventory Audits
Regular hardware and software inventory audits serve multiple essential functions within your organisation. First, they ensure accuracy across all your technology records. Additionally, they verify that your inventory documentation remains current and comprehensive.
Beyond basic record-keeping, audits confirm compliance with various requirements, including:
- Regulatory standards specific to your industry
- Software licensing agreements and usage limitations
- Security protocols and vulnerability management
- Equipment maintenance schedules and lifecycle management
With robust IT asset tracking software, organisations experience markedly improved operational efficiency. These systems illuminate potential resource bottlenecks while ensuring teams have appropriate tools to complete critical tasks effectively.

Executing an Effective IT Quick Audit: Step-by-Step Approach
While IT quick audit procedures might initially appear complex, breaking them into discrete stages makes the process manageable. Follow this structured methodology for optimal results:
1. Strategic Planning
Begin by outlining your audit strategy. Define specific objectives and success criteria. Recognise that hardware and software components may require different assessment methodologies. Incorporate realistic timelines and milestones into your planning documentation.
2. Select Appropriate Technology Solutions
Implementing reliable IT asset audit services dramatically streamlines the entire process. Such platforms significantly reduce manual effort by automating inventory discovery and categorisation. Ideally, select solutions with integrated barcode scanning capabilities to minimise data entry errors. Additionally, these IT asset register systems typically include robust tracking mechanisms proven invaluable for ongoing management.
3. Delegate Responsibilities Effectively
For organisations with substantial technology footprints, distributing audit responsibilities becomes essential. Train designated team members to handle assessment procedures within their respective departments or locations. This approach not only accelerates the audit timeline but ensures specialised knowledge applies to each environment examined.
4. Address Discrepancies Systematically
When managing extensive asset inventories, inconsistencies inevitably emerge. Modern IT asset management audit program solutions simplify resolution by providing detailed analytics highlighting potential issues. These platforms can identify:
- Ghost assets appearing in records but physically absent
- Departmental imbalances in resource allocation
- Underutilised equipment opportunities
- Licensing compliance concerns
- Equipment approaching end-of-life status
Advanced inventory management systems automatically update records when changes occur, providing real-time data access critical for demonstrating regulatory compliance and industry standard adherence.
Developing a Comprehensive IT Asset Management Audit Checklist
Creating a detailed IT asset management audit checklist ensures no critical elements escape examination. Your checklist should include:
Physical Asset Verification
- Confirm existence and location of all hardware components
- Verify serial numbers against existing records
- Assess physical condition and operational status
- Document any unauthorised equipment modifications
Software Compliance Review
- Validate license counts against actual installations
- Identify unauthorised or outdated software
- Document version information and update status
- Confirm regulatory compliance requirements are met
Security Assessment
- Verify security protocols implementation
- Document firmware/software update status
- Identify potential vulnerability points
- Ensure access control mechanisms function properly
Documentation Review
- Update warranty information and service records
- Refresh maintenance schedules as needed
- Review lifecycle replacement planning
- Update responsible party assignments
Understanding what IT assets are, helps organisations build more comprehensive audit protocols tailored to their specific technology environments.

Best Practices for Conducting Computer Auditing
Effective computer auditing transcends basic inventory counts, encompassing comprehensive evaluation of technical infrastructure, organisational processes, and compliance frameworks. Implementing these advanced practices will dramatically improve audit outcomes:
Develop Tiered Audit Frameworks
Rather than applying identical scrutiny to all assets, implement a risk-based tiered approach. Categorise assets by criticality, with mission-critical systems receiving more frequent and intensive examination than standard equipment. This stratification optimises resource allocation without compromising oversight.
Establish Continuous Audit Cycles
Abandon the outdated “annual audit” model in favor of rolling assessment cycles. Schedule monthly micro-audits focusing on specific departments or asset categories, quarterly reviews of critical systems, and annual comprehensive evaluations. This approach distributes workload evenly throughout the year while providing consistent visibility.
Implement Automated Discovery and Reconciliation
Manual inventory procedures inevitably introduce human error at rates of 5-8% even with experienced personnel. Deploy automated network discovery tools that continuously scan for new devices, configuration changes, and software installations. Implement automated reconciliation processes that flag discrepancies between expected and actual inventory for human investigation.
Leverage Geospatial Tracking
Organisations with multiple locations should incorporate geofencing and location-based asset tracking. Modern audit solutions can establish virtual boundaries ensuring assets remain within authorised zones and automatically alert administrators when equipment moves outside designated areas.
Centralise Documentation with Granular Access Controls
Establish a unified asset information repository with role-based access controls. This architectural approach ensures consistent data while limiting modification privileges to authorised personnel. Implement rigorous change management protocols documenting all modifications to asset records, including timestamps and responsible parties.
Incorporate Bi-Directional Feedback Mechanisms
Develop streamlined channels for end-users to report discrepancies, performance issues, or unauthorised equipment. Create automated workflows routing these reports to appropriate IT personnel for validation and resolution. This crowdsourced intelligence often identifies emerging problems before they manifest in formal audit processes.
Implement Comprehensive Trend Analysis
Deploy analytics capabilities examining patterns across multiple dimensions including:
- Mean time between failures for equipment categories
- Software utilisation rates, identifying unused licenses
- Procurement cycle optimisation opportunities
- Security patch compliance across device categories
- Anomaly detection, identifying unusual usage patterns
These multidimensional insights transform audit data from passive record-keeping into strategic decision support.
How To Do An Inventory Audit: Technical Considerations
When planning how to do an inventory audit, several technical factors significantly impact success:
Multi-Protocol Network Discovery Architecture
Modern networks contain diverse device types that communicate via multiple protocols. Implement discovery solutions with comprehensive protocol support including:
- SNMP for network equipment interrogation
- WMI for Windows device scanning
- SSH for Linux/Unix system inventory
- MDM API integration for mobile device assessment
- IPMI for server hardware monitoring
- CDP/LLDP for network topology mapping
Zero-Trust Remote Access Framework
With distributed workforces now standard, establish secure remote audit capabilities built on zero-trust principles. Implement agent-based solutions that provide continuous inventory data regardless of device location while maintaining strong encryption and authentication controls. Create specific audit policies for:
- Home-based workstations and laptops
- Mobile devices accessing corporate resources
- Contractor equipment requiring limited access
- Branch office equipment with intermittent connectivity
Comprehensive Integration Ecosystem
Your audit solution should function as a central hub within your broader technology ecosystem. Establish bidirectional integrations with:
- Procurement platforms enabling automatic asset record creation upon purchase
- CMDB systems maintain configuration relationships
- Help desk platforms associating service history with specific assets
- Financial management systems tracking depreciation and TCO
- Security platforms correlating vulnerabilities with affected assets
- Deployment tools validating standard configurations
- HR systems automating assignment workflows
Advanced Identification Methodologies
Move beyond serial numbers with layered identification strategies:
- RFID/NFC tagging for rapid physical inventory
- MAC address tracking for network presence verification
- Agent-generated hardware fingerprinting resistant to tampering
- QR code generation for field verification via mobile devices
- Biometric association linking equipment to authorised users
Enterprise-Grade Scalability Architecture
Select platforms with demonstrated performance across environments exceeding your projected five-year growth. Evaluate vertical scaling capabilities (handling more assets per instance) and horizontal scaling options (distributed processing across multiple servers). Implement database architecture supporting billions of audit records without performance degradation.

The Evolution of Audit of IT Asset Management
The audit of IT asset management has transformed dramatically in recent years. Advanced, automated solutions that transform how companies track and control technological resources have replaced conventional human spreadsheet methods. This development answers to ever more complicated regulatory standards and reflects larger trends in digital transformation.
Real-Time Monitoring
Continuous monitoring offers ongoing insight into asset condition and location, not point-in-time assessments. Modern systems maintain continual inventory awareness via IoT sensors, RFID tags, and network monitoring. This shift from periodic to continuous auditing enables immediate identification of anomalies and potential security concerns.
Predictive Analytics
Advanced systems now forecast maintenance requirements and replacement needs before failures occur. These systems can forecast component failures weeks or months ahead by analyzing past performance data, usage patterns, and manufacturer specifications. This proactive method reduces disturbance and makes strategic budget planning possible instead of reactive emergency spending.
Compliance Automation
Regulatory reporting that once required extensive manual preparation now generates automatically from properly configured asset management platforms. With regulations like GDPR, HIPAA, and industry-specific requirements becoming increasingly stringent, automated compliance verification provides both efficiency and risk reduction. These systems maintain comprehensive audit trails documenting exactly which assets contain sensitive data and how they’re protected.
Cost Optimization Intelligence
Modern systems identify consolidation opportunities and underutilised resources, driving significant cost savings. Advanced analytics can detect patterns indicating inefficient resource allocation, unnecessary license purchases, or opportunities for standardisation. Organisations implementing these systems typically report 15-30% reductions in ongoing IT expenditures through improved utilisation and strategic procurement.
Cloud Asset Integration
The rapid adoption of cloud resources has necessitated new approaches to asset auditing. Contemporary systems now track virtual instances, containers, and SaaS subscriptions alongside physical equipment. This unified view prevents the shadow IT problems common in organisations maintaining separate tracking systems for physical and virtual resources.
Automated Discovery and Classification
Modern audit systems employ advanced network scanning and artificial intelligence to automatically discover and categorise new assets. These capabilities dramatically reduce manual inventory efforts while improving accuracy. AI-powered classification can identify device types, installed software, and potential security concerns without human intervention.
Maximising Value from Your IT Asset Management Program
Conducting thorough IT asset management audits undeniably requires effort and organisational commitment. However, with appropriate planning, suitable technology solutions, and distributed responsibility models, the process becomes increasingly manageable. Implementing specialised inventory management software transforms what was once an arduous task into a streamlined procedure.
Over time, organisations typically discover that regular audits become progressively less labor-intensive as systems mature. The resulting benefits—enhanced compliance posture, improved resource utilisation, and strengthened security stance—deliver substantive return on the investment required. In today’s technology-dependent business environment, comprehensive asset management isn’t merely good practice—it’s an essential operational foundation.

Try itemit
Choose a better way to track your assets. Start your free 14-day trial now!
Keep Learning
itemit Blog
Tips, guides, industry best practices, and news.
No Results Found
The page you requested could not be found. Try refining your search, or use the navigation above to locate the post.

