Every organisation relies on effective resource management to function smoothly. This is where asset and configuration management plays a pivotal role. By maintaining control over resources, businesses can streamline operations and reduce unnecessary expenses.
Understanding Asset and Configuration Management
Accurate tracking of assets ensures that every tool, system, or device fulfils its purpose without waste. It helps identify gaps, optimise usage, and prevent mismanagement. From physical equipment to digital systems, keeping resources in check enhances productivity and cuts costs.
At the same time, understanding system configurations allows teams to avoid disruptions. When infrastructure components are monitored and organised, teams can respond to changes swiftly and minimise errors.
Together, these practices form a foundation for operational efficiency, ensuring that no resource is overlooked and every system performs at its peak.
Asset Management vs Configuration Management
Understanding the distinction between asset management and configuration management is crucial for maintaining a well-organized IT environment. While both focus on resource control, their objectives and scope differ.
Asset management focuses on tracking and managing the lifecycle of physical and digital assets, such as hardware, software licenses, and other resources. This ensures organisations can optimise asset usage, minimise costs, and plan for future requirements.
In contrast, configuration management deals with maintaining detailed records of IT system configurations. It ensures that servers, networks, and applications are properly documented, enabling teams to track changes, prevent inconsistencies, and maintain system stability.
Many configuration management solutions today leverage cloud-based tools, offering scalable, real-time management of system configurations.
When combined, IT asset and configuration management provides a comprehensive approach to managing IT resources. Asset management ensures every resource is accounted for and used effectively, while configuration management supports seamless system interactions and minimises downtime. Both are foundational to IT service management, helping organisations deliver consistent and reliable services.
Key Differences Between Asset and Configuration Management
To truly grasp the distinction between asset management vs configuration management, It’s helpful to compare their objectives, scope, and practical applications side by side. Below is a comparison chart to clarify their unique roles:
| Aspect | Asset Management | Configuration Management |
| Objective | Tracks asset lifecycle and value of resources like hardware, software, and equipment. | Ensures all system components are configured correctly and work together seamlessly. |
| Scope | Focuses on physical and digital assets, such as computers, licenses, or furniture. | Involves IT infrastructure components like servers, databases, and applications. |
| Data Managed | Ownership details, cost, warranties, depreciation, and usage. | Versioning, relationships between components, and system states. |
| Examples of Use | Tracking laptops assigned to employees or monitoring software licenses for compliance. | Documenting a server’s configuration or mapping relationships between network devices. |
| Primary Goal | Optimise asset usage and reduce costs. | Maintain system consistency and support seamless IT changes. |
In practice, it works like this:
- Asset Management:
A company uses asset management to track all company-issued smartphones. This includes details such as the purchase date, the assigned employee, and warranty information. - Configuration Management:
When deploying a new application, configuration management ensures the server settings, database connections, and network configurations are documented and aligned for proper operation.
The Interplay Between Asset and Configuration Management
Although asset and configuration management serve different purposes, their synergy is what drives efficient IT operations. These practices complement each other by filling gaps in data and providing a complete picture of an organisation’s IT environment.
Asset management answers the “what” and “where” questions: What resources do we own? Where are they located? Meanwhile, configuration management delves into the “how” and “why”: How is a system set up? Why is it configured in a certain way?
For example:
- Asset management might record that a server was purchased last year and is under warranty.
- Configuration management, on the other hand, would detail the server’s operating system, installed applications, and its role in the network.
When these systems work in isolation, information silos emerge. A server might be flagged as functional in the asset database but misconfigured in the system. Integrating the two ensures that assets are not only accounted for but also operational and aligned with the organisation’s needs.
Why Integration Matters
Bringing asset and configuration management together creates a more proactive IT environment:
- Enhanced Visibility: Teams get a unified view of resources and their configurations.
- Faster Issue Resolution: Troubleshooting becomes easier when asset and system configuration details are linked.
- Better Compliance: Accurate data ensures that both licensing and security standards are met.
Organisations that align these practices move beyond simple tracking. They gain control over the entire IT landscape, reducing inefficiencies, improving uptime, and enabling informed decisions.

The Role of Configuration Management Tools
Configuration management tools are essential for maintaining control over IT infrastructure. They automate the monitoring, updating, and documentation of system configurations, ensuring consistency across all components. In ITIL service asset and configuration management, these tools play a dual role: they manage detailed configuration data and integrate it with asset tracking to create a unified and efficient IT environment.
Key Tools for Configuration Management
- Ansible
Ansible is a simple yet powerful tool for automating configuration management and IT operations. It’s agentless, meaning it doesn’t require software installed on client systems, which reduces complexity. Organisations use Ansible to automate repetitive tasks like server setup, software updates, and configuration adjustments. - Puppet
Puppet focuses on defining desired system states and automatically applying those configurations. It uses declarative language to enforce consistency across infrastructure, making it ideal for managing large-scale environments. Its ability to detect and correct configuration drift ensures systems remain secure and compliant. - Chef
Chef uses a code-based approach to manage IT configurations, making it particularly suited for cloud environments. It allows teams to write “recipes” that define how systems should be configured. Chef’s automation streamlines deployments and reduces human error, especially in dynamic, fast-changing infrastructures. - ServiceNow
ServiceNow is a comprehensive platform that supports ITIL processes, including asset and configuration management. It provides a centralised configuration management database (CMDB) to track assets, their relationships, and changes over time. ServiceNow excels in integrating with other IT tools, making it a go-to choice for enterprises aiming for holistic IT management. - itemit
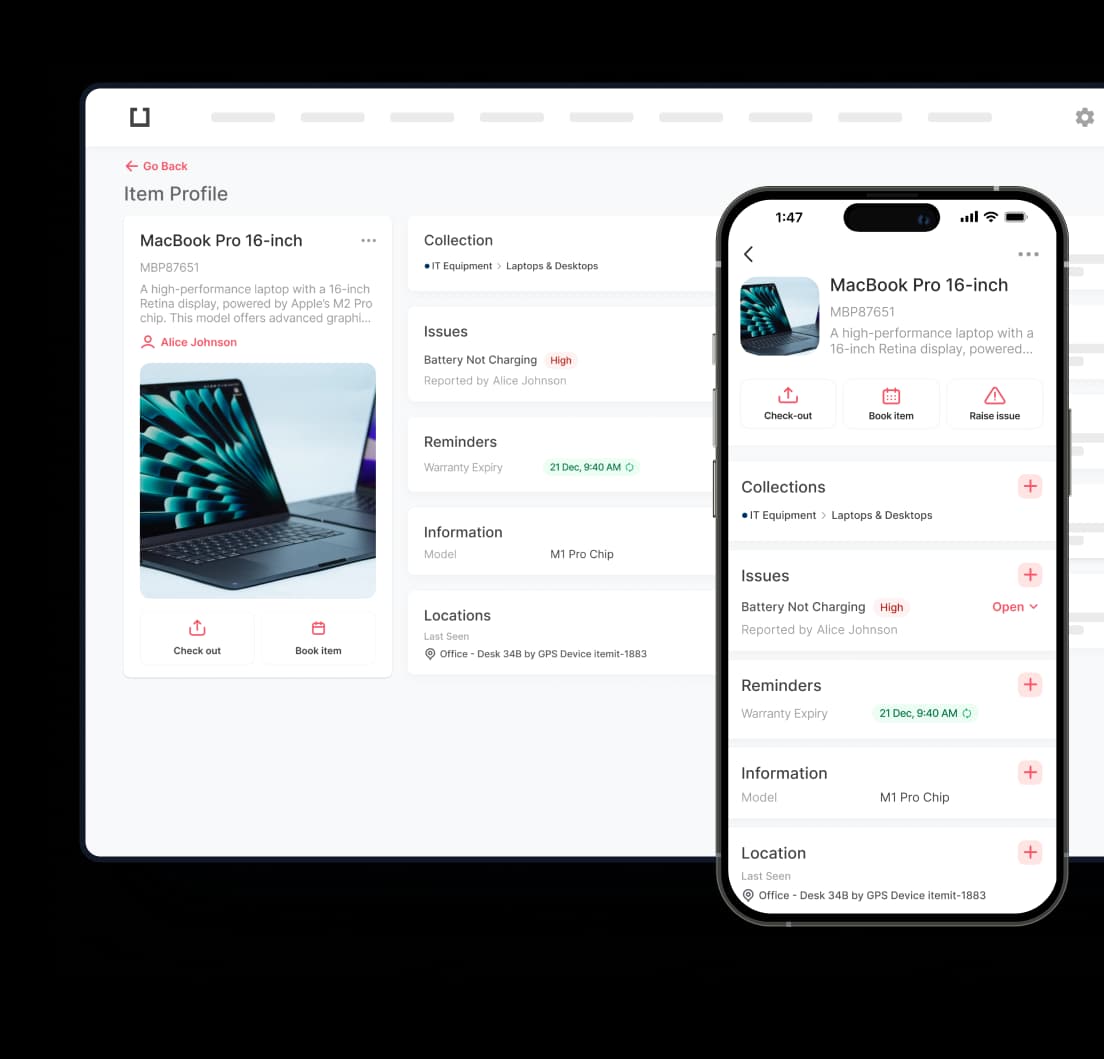
While traditionally seen as an asset management tool, itemit also supports configuration tracking by linking assets with associated metadata, configurations, and dependencies. Its user-friendly interface simplifies tracking for smaller teams, while its powerful integrations make it valuable for ITIL-aligned workflows. itemit bridges the gap between physical asset tracking and IT configuration monitoring, making it versatile for hybrid environments.
How These Tools Enhance IT Management
- Unified Data Management: Tools like ServiceNow and itemit link asset tracking with configuration data, ensuring every resource is properly documented and its role understood.
- Preventive Maintenance: By identifying configuration dependencies, these tools help anticipate potential failures before they impact services.
- Automation and Efficiency: Tools such as Puppet and Chef automate updates and enforce policies, reducing the workload on IT teams while maintaining consistency.
- Improved Decision-Making: Accurate and up-to-date configuration and asset data allow teams to plan upgrades, expansions, or migrations with confidence.
- Regulatory Compliance: Maintaining detailed records of assets and configurations ensures compliance with industry standards and legal requirements.
IT Asset and Configuration Management in Practice
IT professionals rely on IT asset and configuration management to maintain system integrity and ensure operations run smoothly. These practices are not abstract theories—they are hands-on processes that provide clarity, control, and efficiency in managing IT environments.
- Tracking and Managing Assets
IT teams use asset management to maintain a clear inventory of hardware, software, and licenses. This includes details like purchase dates, warranty periods, and current assignments. Accurate tracking prevents resource duplication, reduces waste, and ensures compliance with software licensing agreements. - Monitoring System Configurations
The configuration management process helps IT professionals document and manage the configurations of all system components, such as servers, applications, and network devices. This process ensures systems adhere to organisational standards, with all changes logged for future reference. - Ensuring System Integrity
By combining asset data with configuration details, IT teams can maintain system integrity. For example, if a critical server is due for replacement (tracked through asset management), configuration management ensures that all settings, dependencies, and connections are properly documented and transferred to the new server. - Supporting Change Management
During updates or infrastructure changes, configuration management provides detailed insights into how components interact. IT professionals use this data to plan upgrades, avoid conflicts, and minimise downtime. For instance, before deploying a patch, they can review configuration dependencies to ensure compatibility. - Troubleshooting and Recovery
When issues arise, IT teams rely on both asset and configuration data to identify the root cause. Configuration management reveals recent changes or misconfigurations, while asset management provides information about affected resources. This combined approach speeds up problem resolution and reduces system downtime.
Importance of Asset Configuration Management for Tracking
Effective tracking is critical in IT environments, where even small oversights can lead to disruptions. Asset configuration management addresses this need by integrating configuration data into asset tracking systems, creating a unified approach to managing IT resources.
Improved Visibility
Asset configuration management provides a complete view of both physical and virtual resources. By combining asset details (such as ownership, location, and lifecycle stage) with configuration data (like system settings and interdependencies), IT teams gain deeper insights into their environments. This enhanced visibility helps:
- Quickly identify underutilised or obsolete assets.
- Pinpoint misconfigurations that may lead to performance issues.
- Ensure systems are compliant with organisational standards.
For instance, when managing a fleet of servers, it’s not enough to know their physical location or warranty status. Configuration management adds context, such as installed applications, network roles, and dependency mappings, enabling informed decision-making.
Greater Control
Integrating configuration data into asset tracking systems ensures IT teams can monitor changes and maintain control over their environments. This integration:
- Prevents unauthorised modifications by tracking changes at both asset and configuration levels.
- Reduces downtime by offering clear documentation of dependencies and system relationships.
- Enhances security by identifying and addressing potential vulnerabilities linked to specific configurations.
For example, if a network device is updated with new firmware, asset configuration management ensures the change is logged. IT teams can then verify the update’s compatibility with other components, reducing the risk of disruptions.
Integration in Practice
Modern asset tracking systems increasingly incorporate configuration management features. These systems allow IT professionals to:
- Link configuration details directly to asset records.
- Automate updates when configurations or assets change.
- Generate reports that combine both asset and configuration data for audits or compliance checks.
It enables teams to approach IT management holistically, reducing inefficiencies and improving responsiveness.
Configuration and Asset Management for Effective Asset Tracking
By understanding what digital asset tracking is, businesses can merge configuration management practices to ensure both physical and digital resources are optimised. Combining configuration management with asset management creates a powerful framework for accurate and efficient asset tracking. By integrating these two disciplines, organisations gain a comprehensive view of their resources, enabling them to optimise usage, reduce costs, and prevent operational issues.
How Integration Enhances Asset Tracking
- Unified Data View
Integrating configuration details with asset tracking ensures that every asset has contextual information about its setup, usage, and dependencies. This holistic approach provides IT teams with the insights they need to make smarter decisions and manage resources proactively. - Proactive Maintenance
By linking asset records with configuration data, organisations can monitor both the physical health of an asset and its functional performance. This combination allows for predictive maintenance, minimising downtime and extending the life of critical systems. - Seamless Change Management
When assets undergo upgrades or replacements, configuration data ensures that the transition is smooth. Knowing how an asset is set up and what it connects to helps avoid disruptions during changes or migrations.
When it comes to implementing effective asset tracking, itemit stands out as a comprehensive solution. Designed for both small teams and large organisations, itemit combines the benefits of configuration management with robust asset tracking features.